Medical-surgical nursing can be stressful, overwhelming, and intimidating. This is one good reason why a lot of student nurses don’t like it that much.
However, if you handle stress well and you’re a fast learner, you won’t have a hard time mastering it. In fact, medical-surgical nursing is easy to love as long as you’re self-motivated and committed. The right tips and tricks can help, too.
As a way to help you build an excellent foundation for your nursing practice, here are some really useful medical-surgical nursing mnemonics.
1Acute Myocardial Infarction
An acute myocardial infarction is a heart condition that happens when the blood circulation or flow is abruptly cut off from the heart. The break in circulation lasts long enough to cause tissue damage or death.
Risk factors of myocardial infarction include high blood pressure, high triglyceride and cholesterol, obesity, diabetes or high blood sugar, smoking, sedentary lifestyle, unhealthy diet and being under too much stress.
The early sign of an acute myocardial infarction is angina which is chest pain provoked by ischemia. Signs and symptoms include anxiety, cough, dizziness, fast heart rate, heaviness in or across the chest, pain in the chest, back, jaw, and other areas of the upper body, shortness of breath and sweating.
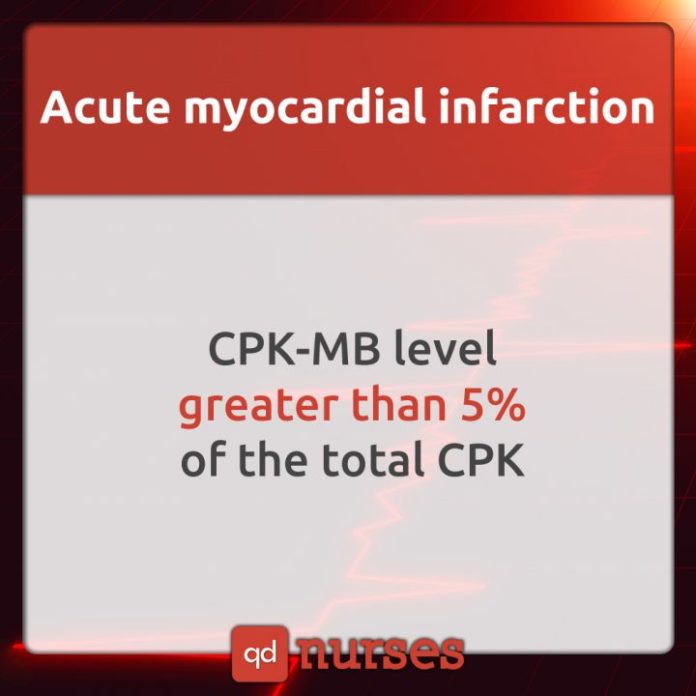
Creatine phosphokinase, Muscle Band or the CPK-MB test is used to assist diagnoses of an acute myocardial infarction. It measures the blood level of CK-MB, the bound combination of two variants (isoenzymes CKM and CKB) of the enzyme phosphocreatine kinase.
CK is a muscle enzyme. There are 3 types: CPK-MM, which is found in skeletal muscles, CPK-MB, which is found in the heart, and CPK- MM, which is found in the brain. CPK-MB levels rise three to six hours after a heart attack. Elevated levels may also be due to electrical injuries, heart defibrillation, heart injury, inflammation of the heart muscle usually due to a virus (myocarditis) and open heart surgery. CPK-MB levels do not usually rise with chest pain caused by angina, pulmonary embolism or congestive heart failure.
2Signs of Neurovascular Compromise
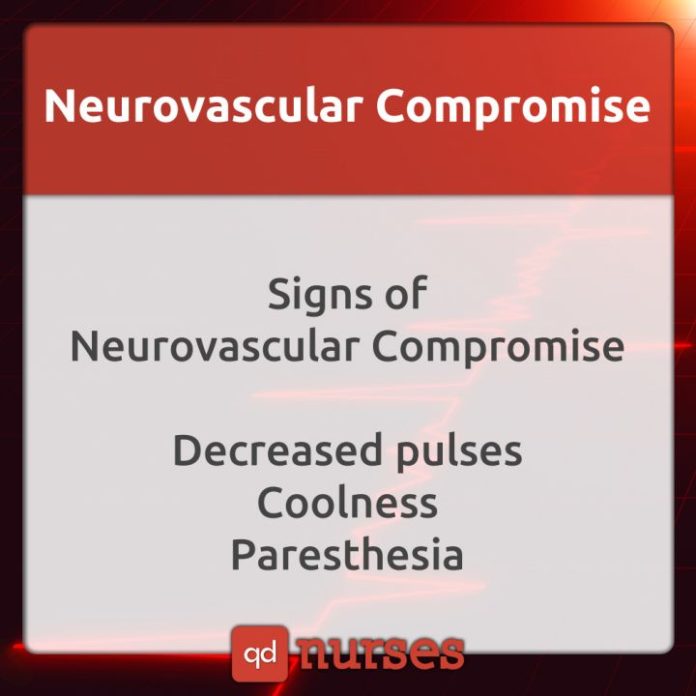
Neurovascular compromise occurs when there are physiological indicators of injury to blood vessels or nerves. Signs include pallor, loss of palpable pulses, paralysis, paresthesia, coolness, and severe pain.
3Addison’s Disease & Cushing Syndrome

Addison’s disease is a disorder that occurs when the body produces insufficient amounts of adrenal hormones. It happens when the adrenal glands are damaged, producing insufficient amounts of the hormone cortisol and aldosterone. It occurs in all age groups and affects both sexes and can be life threatening.
Symptoms of Addison’s disease may include muscle weakness and fatigue, weight loss and decreased appetite, skin darkening, low blood pressure, fainting, salt craving, low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, muscle or joint pains, irritability, depression, body hair loss, and sexual dysfunction in women.
Also Read: Nursing Mnemonics & Acronyms (Endocrine System)
Cushing syndrome, on the other hand, is a disorder that occurs when the body has a high level of the hormone cortisol. It is usually caused by taking too much glucocorticosteroid medications like prednisone, dexamethasone, and prednisolone. Some people develop Cushing syndrome because their bodies produce too much cortisol, which is a hormone made in the adrenal glands. Too much cortisol may be caused by a tumor of the adrenal gland, a tumor elsewhere in the body that produces corticotropin-releasing hormone and/or ACTH.
Symptoms of Cushing’s syndrome include round, red, full face (moon face); slow growth rate in children; weight gain with fat accumulation on the trunk, but fat loss in arms, legs, and buttocks (central obesity); skin infections; purple marks called striae on the skin of the abdomen, thighs, and breasts; thin skin with easy bruising; backache which occurs with routine activities; bone tenderness; weak muscles; mental changes; fatigue; headache; increased thirst and urination.
To diagnose Cushing syndrome, laboratory tests may be required. These include tests for blood cortisol levels, blood sugar, and saliva cortisol levels; dexamethasone suppression test; 24-hour urine for cortisol and creatinine; ACTH level and ACTH stimulation test.
4Anticholinergic Effect

Anticholinergics are medications used to block the action of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine in the brain. These drugs are used to treat conditions like asthma, incontinence, gastrointestinal cramps, and muscular spasms. However, they are also prescribed for depression and sleep disorders. They help block involuntary movements of muscles associated with these diseases and they balance the production of dopamine and acetylcholine.
Anticholinergics are usually not prescribed to people with conditions like myasthenia gravis, hyperthyroidism, glaucoma, enlarged prostate, hypertension, blockage of the urinary tract, increased heart rate (tachycardia), heart failure, severe dry mouth, hiatal hernia, severe constipation and liver disease.
The side effects of anticholinergics include dry mouth, blurred vision, constipation, drowsiness, sedation, hallucinations, memory impairment, difficulty in urinating, confusion, delirium, decreased sweating and decreased saliva.
5ARDS & DIC

Acute respiratory distress syndrome occurs when fluid builds up in the alveoli. More fluid in the lungs means less oxygen can reach the bloodstream, thus, depriving the organs of the oxygen they need in order to function. It usually occurs in people who are critically ill.
The main symptom of ARDS is severe shortness of breath which develops within a few days after the original disease or trauma. Other signs and symptoms of ARDS include labored and unusually rapid breathing, low blood pressure, confusion and extreme tiredness.
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) is a condition wherein blood clots form throughout the body’s small blood vessels. These clots may reduce or block blood flow through the blood vessels, which can damage the body’s organs.
Symptoms of DIC are often those of an underlying condition such as sepsis or severe infection, trauma, organ destruction, solid tumors, myeloproliferative or lymphoproliferative malignancies, obstetric calamities like amniotic fluid embolism and abruptio placentae, vascular abnormalities like Kasabach-Merritt syndrome and large vascular aneurysms, severe hepatic failure, and severe toxic or immunologic reactions.
6Autonomic Dysreflexia

Autonomic Dysreflexia (AD), also known as hyperreflexia, refers to an over-active autonomic nervous system which causes an onset of excessively high blood pressure
Triggers for autonomous dysreflexia in persons with spinal cord injuries include a distended bladder, blocked catheter, urinary retention, urinary tract infection, bladder stones, constipation, bowel impaction, hemorrhoids, skin irritations, pressure sores, and tight clothing.
Symptoms include anxiety and apprehension, irregular or racing heartbeat, nasal congestion, high blood pressure (with systolic readings often over 200 mmHg), pounding headache, flushing of skin, profuse sweating, lightheadedness, dizziness or confusion, and dilated pupils.
7Beck’s Triad

Beck’s Triad refers to three medical signs that indicate cardiac tamponade. Cardiac tamponade is a life threatening medical condition in which blood or fluids fill the space between the sac that encases the heart and the heart muscle, placing extreme pressure on the heart.
The pressure prevents the ventricles from fully expanding, thus, keeping the heart from functioning properly. The heart then will not be able to pump enough blood to the rest of the body, which can lead to organ failure, shock, and even death. Beck’s triad includes distant heart sounds, distended jugular veins, and decreased arterial pressure.
8Bell’s Palsy

Bell’s palsy refers to the paralysis or weakness of the muscles on one side of the face. Damage to the facial nerve that controls muscles on one side of the face causes that side of the face to droop. It is not the result of a stroke or a transient ischemic attack; instead, most cases are caused by the herpes virus.
Symptoms include sudden weakness or paralysis on one side of the face, drooling, eye problems such as excessive tearing or a dry eye, loss of ability to taste, pain in or behind the ear, numbness in the affected side of the face, and increased sensitivity to sound.
9Blood Sugar

mellitus often leads to frequent elevated blood sugar levels, which, in time, damages the body and may lead to several other health problems such as damage to the eyes, kidneys and nerves. It can even cause heart disease, stroke and the need to remove a limb. A blood test can show if someone has diabetes.
Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) are the two most common, yet threatening, diabetes-related emergencies.
Symptoms of hypoglycemia include cold, clammy skin, trembling or feelings of nervousness, lack of motor coordination and fatigue, irritability or confusion, blurred vision, headache or dizziness, nausea or stomach pain, and fainting or unconsciousness.
On the other hand, the symptoms of hyperglycemia include increased thirst and urination, sweet odor to the breath, fatigue, agitation and confusion, high levels of ketones in the urine, and weight loss.
10Cholecystitis

Cholecystitis is the inflammation of the gallbladder which is commonly caused by a gallstone stuck in the cystic duct. The gallstone blocks the flow of fluid out of the gallbladder, which results in an irritated and swollen gallbladder. Other causes include infection or trauma.
Common signs and symptoms of cholecystitis is pain in the upper right abdomen that may radiate to the back or right shoulder blade; nausea and vomiting; fever; and pain that gets worse during a deep breath.
11Chronic Kidney Disease Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD.

Chronic Kidney Disease Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD) occurs when the kidneys fail to maintain the proper levels of calcium and phosphorus in the blood. CKD-MBD is usually manifested by one of the three components: abnormalities of Calcium, Phosphorus, Parathyroid Hormone (PTH), or Vitamin D metabolism; abnormalities in bone turnover, mineralization, volume linear growth, or strength; and extraskeletal calcification.
12Compartment Syndrome

Compartment syndrome occurs when injury causes generalized painful swelling and increased pressure within a compartment which may lead to lack of oxygen and nutrients to the muscles and nerves.
Symptoms include persistent deep ache in an arm or leg, pain that seems greater than expected for the severity of the injury, numbness, pins-and-needles or electricity-like pain in the limb, swelling, tightness and bruising.
13Creatinine

Creatinine is a chemical waste molecule that is generated from muscle metabolism. It is produced from creatine and is transported through the bloodstream to the kidneys. The kidneys normally maintain the blood creatinine which is found to be a reliable indicator of kidney function. An elevated creatinine level signifies impaired kidney function or kidney disease.
14CSF in Meningitis

Meningitis refers to the inflammation of the lining around the brain and the spinal cord which is usually caused by an infection from viruses (Viral meningitis) or bacteria (Bacterial meningitis). It is contagious and can be passed from one person to another through coughing, sneezing and through close contact.
The most common symptoms include a stiff or painful neck, fever, headache, vomiting, trouble staying awake, and seizures. The most important laboratory test for meningitis is the lumbar puncture or the spinal tap wherein a sample of fluid is removed from around the spine and tested to see if it contains organisms that cause the illness.
In meningitis, the fluid (CSF) is usually high in protein and low in glucose. Other tests include blood tests, CT scan, and MRI.
15Diverticulitis

Diverticulitis refers to a condition where the diverticula, the small, bulging pouches that form in the lining of the digestive system, become inflamed or infected. It can cause severe abdominal pain, fever, nausea and a marked change in bowel habits.
Symptoms include belly pain, usually in the lower left side, that sometimes worsens when you move. Other symptoms include fever and chills, bloating and gas, diarrhea or constipation, nausea and sometimes vomiting, and loss of appetite.
Patients who have diverticulitis must be on low residue diet. Surgery is necessary only if diverticulitis doesn’t get better with other treatment, or if there are other conditions such as long-lasting (chronic) pain, a bowel obstruction, a fistula, or a pocket of infection (abscess).
16Dumping Syndrome

Dumping syndrome is a group of symptoms that usually occur after having part of the stomach removed. Symptoms include a feeling of fullness even after eating just a small amount, abdominal cramping or pain, nausea or vomiting, severe diarrhea, sweating, flushing, light-headedness, and rapid heartbeat.
The symptoms of the late phase of dumping syndrome include fatigue or weakness, flushing or sweating, shakiness, dizziness, fainting or passing out, loss of concentration or mental confusion, feelings of hunger, and rapid heartbeat.
17Erythropoietin

Erythropoietin is the hormone produced in the kidneys that influences the rate of production of red blood cells (erythrocytes). When the number of red blood cells decreases or when the oxygen transported by the blood diminishes, a sensor detects the changes and the production of erythropoietin is increased.
18Fractured Hip

A hip fracture is a fracture in the upper portion of the thigh bone or femur. It is a serious condition, and always requires surgery. The usual causes of a hip fracture include falls to a hard surface or from a great height, blunt trauma to the hip such as from a car crash, diseases such as osteoporosis, and obesity.
19Functions of the Kidney

The kidneys are located near the middle of the back, just below the ribcage. They process blood to sift out waste products and excess water every day. The waste and water become urine, which flows to the bladder through the ureters.
The major functions of the kidneys include filtering out wastes to be excreted in the urine, regulating blood pressure via both urinary excretion of wastes and initiating the renin-angiotensin hormone regulatory system, regulating an acid-base balance via the bicarbonate system, and stimulating red blood cell production via the release of the hormone erythropoietin.
20Galeazzi Sign

A positive Galeazzi sign indicates fracture in the neck of the femur. To identify this sign, the patient is placed in supine position with hips flexed 45 degrees and knees flexed 90 degrees. The height of the patellae from the foot of the table is then observed, as well as femoral length discrepancies.
21Gastric Ulcer

Gastric ulcer is a localized area of erosion in the stomach lining. It usually results in abdominal pain, bleeding, and other gastrointestinal symptoms.
The most common cause is an infection in the stomach associated with the bacteria Helicobacter pylori. Other causes include prolonged use of painkillers called non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and gastrinomas which are tumors of the acid-producing cells of the stomach that increases acid output.
Symptoms usually include a gnawing or burning pain in the middle or upper stomach between meals or at night, bloating, heartburn, nausea or vomiting, dark or black stool (due to bleeding), vomiting blood (that can look like “coffee-grounds”), weight loss, and severe pain in the mid to upper abdomen.
22Gastroenteritis

Gastroenteritis refers to the inflammation of the lining of the stomach and small and large intestines, which is usually caused by an infection or ingestion of toxins or drugs. Symptoms usually include diarrhea, abdominal pain, vomiting, headache, fever and chills.
23Glomerulonephritis

Glomerulonephritis is the inflammation of the glomeruli, which normally remove excess fluid, electrolytes and waste from the bloodstream and pass them into the urine.
Signs and symptoms of glomerulonephritis include pink or cola-colored urine (hematuria), foamy urine due to excess protein (proteinuria), high blood pressure (hypertension), fluid retention (edema) with swelling evident in the face, hands, feet and abdomen, and fatigue from anemia or kidney failure.
24Guillain-Barre Syndrome

Guillain-Barre syndrome is a disorder in which the body’s immune system attacks the nerves. It is very rare, and the first symptoms are usually weakness and tingling sensation in the extremities.
Signs and symptoms may include prickling, “pins and needles” sensations in your fingers, toes, ankles or wrists; weakness in your legs that spreads to your upper body; unsteady walking or inability to walk or climb stairs; difficulty with eye or facial movements, including speaking, chewing or swallowing; severe pain that may feel achy or cramp-like and may be worse at night; difficulty with bladder control or bowel function; rapid heart rate; low or high blood pressure; and difficulty breathing.
25Hemophilia

Hemophilia is a rare inherited disorder in which the blood doesn’t clot normally because it lacks sufficient blood-clotting proteins (clotting factors). If the deficiency is severe, spontaneous bleeding may be experienced.
Signs and symptoms of spontaneous bleeding include unexplained and excessive bleeding from cuts or injuries, or after surgery or dental work; many large or deep bruises; unusual bleeding after vaccinations; pain, swelling or tightness in the joints; blood in urine or stool; nosebleeds without a known cause; and in infants, unexplained irritability.
Emergency signs and symptoms include sudden pain; swelling and warmth in large joints, such as knees, elbows, hips and shoulders, and in arm and leg muscles; bleeding from an injury, especially if there is a severe form of hemophilia; painful, prolonged headache; repeated vomiting; extreme fatigue; neck pain; and double vision.
26Cystic Fibrosis

Cystic fibrosis is an inherited disorder that causes severe damage to the lungs and the digestive system and affects the cells that produce mucus, sweat and digestive juices. These bodily fluids are usually thin, but in cystic fibrosis, a defective gene causes the secretions to become thick and sticky, so instead of acting as a lubricant, the secretions block the tubes, ducts and passages.
Signs and symptoms vary, but they usually include a persistent cough that produces thick sputum and mucus, wheezing, breathlessness, a decreased ability to exercise, repeated lung infections, inflamed nasal passages or a stuffy nose, foul-smelling and greasy stools, poor weight gain and growth, intestinal blockage particularly in newborns (meconium ileus), and severe constipation.
27Hiatal Hernia

In a hiatal hernia, the upper part of the stomach slips through the diaphragm and into the chest. Common symptoms include heartburn that gets worse when you lean over or lie down, chest pain, trouble swallowing, and belching. Emergency symptoms include nausea, vomiting, and the inability to pass gas or empty bowels.
28ICP & Shock
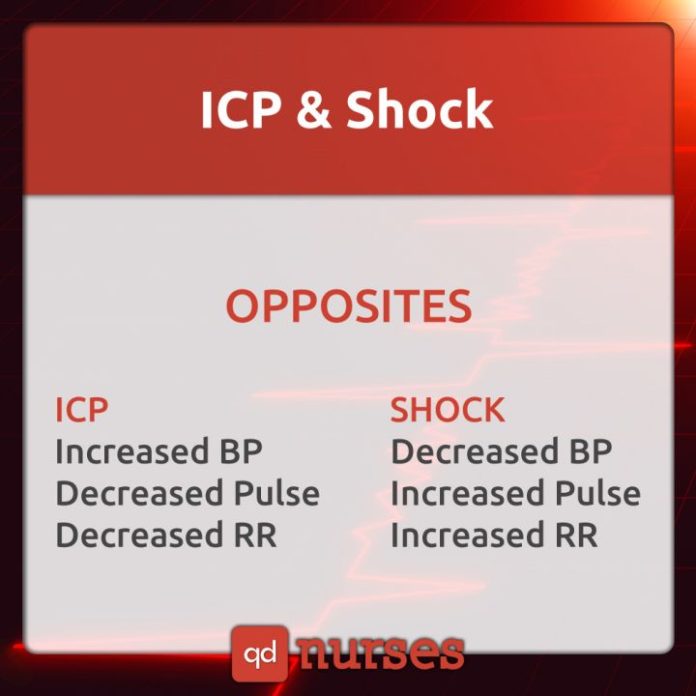
Increased Intracranial Pressure may be caused by a mass (tumor), bleeding into the brain or fluid around the brain, or swelling within the brain itself. Shock, on the other hand, occurs when there is not enough circulating blood, which can lead to multiple organ damage, and may cause serious complications, such as heart failure.
Signs and symptoms of shock include decrease in blood pressure, rapid, weak or absent pulse, irregular heart rate, confusion, cool and clammy skin, rapid and shallow breathing, anxiety, lightheadedness, decrease in urine output, chest pain, nausea, thirst and dry mouth, low blood sugar, dilated pupils or lackluster eyes, fever in septic shock, and hives and swelling of the face and throat in the anaphylactic shock.
29Intussusception

Intussusception refers to the condition in which a part of the intestine is pulled inward into itself, making it difficult for food to pass through. Symptoms usually include blood and mucus in the stool, vomiting, a lump in the abdomen, and lethargy.
30Locked-in Syndrome

Locked-in Syndrome is a rare neuromuscular disorder which involves total paralysis of voluntary muscles except for the eye muscles. It can be caused by a traumatic brain injury or a neurological condition. Symptoms include paralysis of voluntary muscles and inability to speak.
31Necrotizing Enterocolitis

Necrotizing Enterocolitis refers to an idiopathic injury of the inner surface of the intestine, which usually occurs in premature babies.
Newborns with necrotizing enterocolitis may develop swelling of the abdomen. They can also vomit bile-steamed intestinal fluid, and there may be blood in the stools.
32Pancreatitis

Pancreatitis is the inflammation of the pancreas, which may be caused by gallstones, alcohol, various drugs, certain viral infections, and digestive enzymes.
Signs and symptoms of acute pancreatitis often include upper abdominal pain that radiates to the back or worsens after eating, nausea, vomiting, and tenderness when touching the abdomen.
Signs and symptoms of chronic pancreatitis, on the other hand, include upper abdominal pain, weight loss without trying, and oily, smelly stools.
33Pernicious Anemia

Pernicious anemia is an autoimmune disorder in which the body fails to make enough healthy red blood cells. Common symptoms include weakness, headaches, chest pain, and weight loss. Pallor, sore tongue and increased heart rate may also be noted.
34Reiter’s Syndrome

Reiter’s Syndrome, or Reactive Arthritis, is a form of arthritis which may cause inflammation and pain in the joints, the skin, the eyes, the bladder, the genitals, and the mucous membrane. Causes may include exposure to Chlamydia or other bacteria such as Salmonella, Shigella, Yersinia, or Campylobacter.
35Signs of Renal Failure

Signs of renal failure include weakness, shortness of breath, lethargy, confusion, and generalized swelling.
Blood tests that measure levels of creatinine and urea nitrogen in the blood are needed to confirm the diagnosis. A progressive rise in creatinine indicates acute kidney injury. The level of creatinine is also one of the best indicators of the degree or severity of the decline in kidney function.
Other blood tests may determine metabolic imbalances that occur if the decline in kidney function is severe, such as increase in blood acidity, phosphorus, and potassium levels, and decrease in magnesium and sodium levels.
36Retinopathy

Retinopathy is a condition wherein the blood vessels of the retina are damaged. It is usually a sign of an underlying medical condition such as diabetes and hypertension.
There may be no symptoms in the early stage, but as the disease progresses, symptoms may include blurred vision, floating spots, blind spots, changes in color perception, sudden loss of vision, double vision, and eye pain.
37Shock vs. Increased ICP

Increased Intracranial Pressure is a rise in pressure around the brain, which may be caused by an increased cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) or blood due to an injury or a ruptured tumor. Signs and symptoms include headaches, nausea, vomiting, increased blood pressure, decreased mental abilities, confusion, double vision, shallow breathing, pupils that are not responsive to the changes in light, seizures, loss of consciousness, and even coma.
Shock may be due to trauma, heat, blood loss, an allergic reaction, severe infection, poisoning, and severe burns. Signs and symptoms include cool and clammy skin, weak and rapid pulse, nausea, lackluster eyes, and decrease in blood pressure.
38Sickle Cell Crisis

A sickle cell crisis is pain that can begin suddenly and last several hours or days. It occurs when sickled red blood cells block small blood vessels that carry blood to the bones. Symptoms include dull, sharp, throbbing, or stabbing pain in the back, knees, legs, arms, chest, or stomach. The most important management to a patient experiencing sickle cell crisis is pain relief.
39Toxic Shock Syndrome

Toxic shock syndrome is a group of severe symptoms, including dangerously low blood pressure, usually caused by toxins produced by staphylococci (and sometimes streptococci).
Symptoms usually start with a fever of 102 to 105 degrees Fahrenheit, followed by severe headaches, sore throat, red eyes, extreme tiredness, confusion, vomiting, profuse watery diarrhea, and a sunburn rash all over the body.
40Twitching

Muscle twitches may occur due to dehydration, caffeine overdose, and imbalance in electrolytes such as calcium, magnesium and sodium.
An imbalance in electrolytes may be the result of fluid loss from vomiting or diarrhea, excessive sweating or inadequate dietary intake.
41Treatments for Ventricular Tachycardia

Ventricular Tachycardia (VT) is a condition in which the ventricles of the heart beat very quickly. VT may lead to ventricular fibrillation, which may cause the heart to fail and lead to death if not treated promptly. Symptoms include palpitations, dizziness or lightheadedness, shortness of breath, chest pain, syncope, and weak or absent pulse.
42Virchow’s Triad

Virchow’s triad presents three factors that are known to contribute to thrombosis. The triad basically consists of alterations in normal blood flow, injuries to the vascular endothelium, and alterations in the constitution of blood, or hypercoagulability. The triad was first formulated in 1856 by a German physician named Rudolf Virchow (1821-1902).
43Postoperative Bleeding

Postoperative care refers to the care given to a patient following a surgical procedure. It begins in the recovery room and continues throughout the recovery period.
The most critical concerns in postoperative care are airway clearance, pain control, mental status, and wound healing. Preventing urinary retention, constipation, deep venous thrombosis, and BP variability (high or low) are also prioritized.
Postoperative complications include primary hemorrhage, basal atelectasis, shock, and low urine output, acute confusion, nausea and vomiting, fever, secondary hemorrhage often due to infection, pneumonia, wound or anastomosis dehiscence, deep vein thrombosis, acute urinary retention (early stage), bowel obstruction, incisional hernia, persistent sinus, recurrence of reason for surgery, and keloid formation (late stage), among others.
Late postoperative bleeding occurs several days after surgery and usually occurs when an infection damages vessels at the surgery site.
44Pain Withdrawal

Deterioration simply means to become worse. To recognize patient deterioration, one always needs to observe and monitor the patient, acknowledge deterioration, call for help, and ask for expert intervention if needed. One common sign of deterioration is the patient’s withdrawal from painful stimuli.
Signs and symptoms for airway/breathing deterioration include tachypnea and retractions (early stage), tachypnea and diminished breath sounds (late stage), and gasping, ineffective breathing or no respiratory effort (arrest).
Signs and symptoms for circulation deterioration include tachycardia, pale and cool extremities, normal blood pressure, oliguria (early stage), cyanosis and hypotension (late stage), and bradycardia, weak thready pulse, arrhythmia, and no cardiac contractions (arrest).
Signs and symptoms for Central Nervous System include irritability, restlessness, lethargy (early stage), stupor (late stage), and unresponsive, flaccid, and tonic posturing (arrest).
45Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia

Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia is a fast heart rate that begins and ends abruptly. The condition originates in heart tissue other than that in the ventricles and is often associated with symptoms such as weakness, light-headedness, shortness of breath, and chest pain.
Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia happens when electric signals starting in the atria fire irregularly. This adversely affects the signals transmitted from the sinoatrial node which is the heart’s natural pacemaker. This in turn speeds up the heart rate and prevents the heart from having enough time to fill the blood before pumping out, which means that there won’t be enough blood or oxygen transported throughout the body.
Episodes of Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia may often be stopped by one of several maneuvers that stimulate the vagus nerve. These include straining as if having a difficult bowel movement, rubbing the neck just below the angle of the jaw (which stimulates a sensitive area on the carotid artery called the carotid sinus), and plunging the face into a bowl of ice-cold water.
These maneuvers are most effective when they are used shortly after the arrhythmia starts. Otherwise, people are advised to seek medical intervention to stop the episode.
Adenosine is a short-acting medication that is commonly used as a first-line drug to treat Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia. Other treatment options for other atrial tachycardias include calcium channel blockers, beta blockers, digoxin, and amiodarone.
46Pyloric Stenosis

stenosis is a condition affecting the opening between the stomach and small intestine in infants. It causes the pylorus muscles to thicken, blocking the food from entering the baby’s small intestine. This disorder can lead to forceful vomiting, dehydration, and weight loss. Pyloric stenosis can be fixed with surgery.
47Types of Renal Failure

Renal failure is the temporary or permanent damage to the kidneys which results in loss of normal kidney function. There are two types of renal failure: acute and chronic.
Acute Renal Failure is a condition in which the kidneys have suddenly stopped working and is potentially reversible. Symptoms include little or no urine, swelling, loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting, confusion, anxiousness, restlessness, sleepiness, and flank pain. Acute kidney injury is most often diagnosed during the patient’s hospital stay for another cause.
Chronic Renal Failure, on the other hand, means that for some time, the kidneys have not been working the way they should. It progresses slowly over at least three months and it may lead to permanent kidney damage. Symptoms of chronic kidney disease may not develop until very little kidney function remains. Causes usually include chronic hypertension, diabetes, kidney diseases and infections, a narrowed or blocked renal artery, and long-term use of nephrotoxic drugs.
See More:
Nursing Flashcards (Communicable Diseases)
Nursing Flashcards (Diagnostics and Lab Procedures)
Nursing Flashcards (Fundamentals of Nursing)
Nursing Flashcards (NCLEX Tips/Psychiatric Nursing)
Nursing Flashcards (Nutrition)
Nursing Flashcards (Obstetrics and Newborn Care)
Nursing Flashcards (Pediatric Nursing)
Nursing Flashcards (Pharmacology)