1. Pain Assessment — “PQRST.”
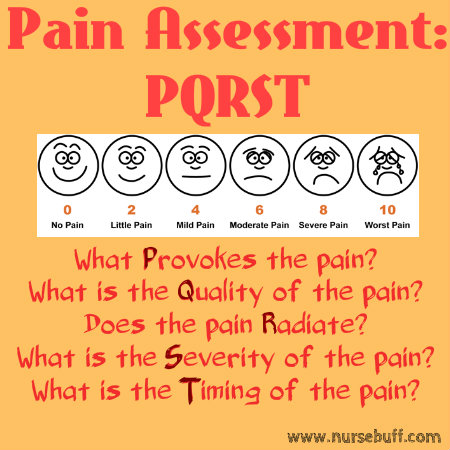
Nurses need a systematic approach to pain assessment and evaluation in order to improve the well-being of their patients.
When assessing pain, nurses need to ask what provokes the pain, it’s quality, whether it radiates or not, it’s severity, as well as it’s timing.
2. Pain Management — “ABCDE.”
Pain management always starts with patient assessment. You can then provide the patients with options for pain relief, deliver the possible interventions and enable the patient to have pain control. These steps may be remembered through the acronym “ABCDE.”
3. Hypersensitivity Reaction Types — “ACID.”
Hypersensitivity means there is a heightened response in a body tissue to an antigen or a foreign body. Normally, the body responds to an antigen by producing certain antibodies. The resulting immune response may lead to cell damage. Substances released from damaged cells called histamines cause dilation of small blood vessels, tissue inflammation, and constriction of the bronchi of the lungs.
4. Right Lower Quadrant Pain Possibilities — “APPENDICITIS.”
The right lower quadrant contains the large and small intestines, as well as the appendix and the ovaries (in female patients). The right upper quadrant, on the other hand, contains the liver, gallbladder, tail of the pancreas, the right kidney and its adrenal gland.
Pain or tenderness in the right upper quadrant may reveal kidney disease, while pain when palpating the right lower quadrant may indicate appendicitis.
In the left upper quadrant, you will find the stomach, spleen, head of the pancreas and the left kidney with adrenal gland. The left lower quadrant contains the left ovary and the uterus in female patients.
Any masses upon palpation in the left lower quadrant may indicate uterine fibroids or ovarian tumors, while the spleen may be palpated over the left upper quadrant only if it is enlarged.
5. Post-operative Fever Etiologies — 5 W’s.
Post-operative fever is a condition wherein there is an abnormally high temperature following a surgical procedure. Factors that may cause post-operative fever are the following: Wind (pneumonia and atelectasis), Wound (surgical incision infections), Water (urinary tract infection), Walking (deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolus) and Wonder-drugs (especially anesthesia).
6. Causes of Dementia and Delirium — “DEMENTIA.”
Dementia is defined as the loss of mental functions such as thinking, memory, and reasoning, which is severe enough to interfere with a patient’s daily functioning. It is not a disease, rather a group of symptoms that are caused by several conditions. There may also be changes in personality, mood and behavior.
Delirium, on the other hand, is defined as an acute change in cognition and a disturbance of consciousness. Patients suffering from delirium may fall in and out of consciousness and there may be problems with awareness, attention, emotions, muscle control, sleeping and waking.
Remember: Delirium has a rapid onset and is temporary while dementia is progressive and often secondary to chronic neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease.
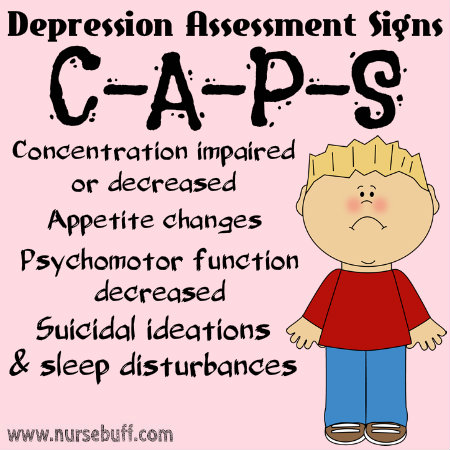
7. Depression Assessment Signs — “CAPS.”
Depression refers to a very low mood which can be severe enough to interfere with daily life activities. Signs of depression can be remembered with the acronym C-A-P-S (Concentration impaired or decreased, Appetite changes, Psychomotor functions decreased and Suicidal ideations and sleep disturbances).
Other symptoms include tiredness or fatigue, feelings of worthlessness, agitation, and slowing of movements.
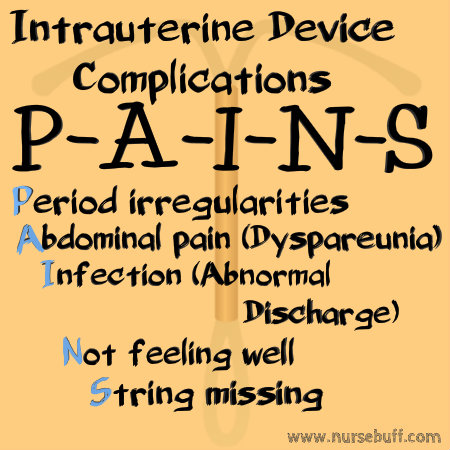
8. Intrauterine Device Complications — “PAINS.”
An intrauterine device is a small device that fits inside a woman’s uterus, and works by preventing fertilization of the egg. It is one of the most effective contraceptive methods and contains no hormones, which means it can be used even while breastfeeding.
However, complications may still arise when using an intrauterine device. These complications are best remembered using the acronym P-A-I-N-S (Period irregularities, abdominal pain and dyspareunia, infection, fever or chills and a missing string).
9. Sprains and Strains Nursing Care — “RICE.”
A sprain is an injury that usually involves small tears of the ligaments and joint capsule. A strain, however, is an injury that affects tendons or muscles. Symptoms include pain, swelling, stiffness and reduced functioning.
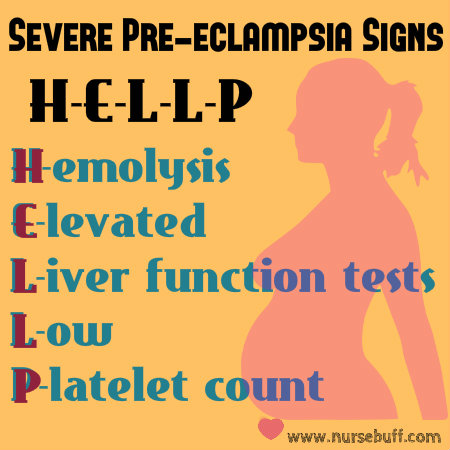
10. Severe Pre-Eclampsia Signs — “HELLP.”
Pre-eclampsia is a pregnancy complication characterized by high blood pressure and signs of damage to organ systems. If left untreated, it may lead to even more serious complications for both the mother and the baby.
Pre-eclampsia usually starts after 20 weeks of pregnancy in a woman whose blood pressure had usually been normal. Even a slight rise in the blood pressure may indicate pre-eclampsia.
11. Hematology — 3 Rules.
These rules can be used to check if the Complete Blood Count on your patient’s results are valid. Though these rules may not be completely flawless, they can still be tools used to further investigate sample integrity and/or instrument operation. Some institutions require a review of the indicates using the Rules of Three. For instance, the Hct must match the Hb x 3 +/-3, or further investigation may be required.
12. Hematuria Causes — “HEMATURIAS.”
Hematuria is the presence of red blood cells in the urine. Sometimes, the urine can become pink, red, or cola-colored, but there are some cases when there is not enough blood in the urine to cause a color change.
Possible causes of hematuria may be summarized using the acronym H-E-M-A-T-U-R-I-A-S: Hemorrhagic diseases, Endocarditis, Malignant Hypertension, Acute Glomerulonephritis, Renal Tuberculosis or Tumor in the bladder, Urinary Tract Infection, Renal Infarct, Idiopathic causes, Anti-coagulants and Stones in the Urinary Tract.