Pharmacology isn’t the easiest to study and master. Apart from drug names, you also have to know what they do, how they interact with each other, and who they are for. You also need to know how much the body can take and what can happen if a patient takes more than what’s necessary.
As a student nurse, these things can easily make you feel overwhelmed.
As a way to help you, we’ve created this list of pharmacology mnemonics you’ll find handy when studying and preparing for exams.
1Aspirin

Aspirin is a salicylate drug that has anti-inflammatory, analgesic, anti-pyretic and anti-platelet effects.
It is commonly used to relieve acute symptoms like fever, pain and inflammations. It also has anti-platelet effects as it inhibits the production of thromboxane.
In using aspirin, side-effects like tinnitus, stomach pain, GI bleeding and thrombocytopenia should be monitored.
Study Guides:
What is Aspirin? – Patient.co.uk
acetylsalicylic acid, Aspirin, Ecotrin – MedicineNet.com
2Insulin

When mixing insulin, the clear one should be drawn before the cloudy one. The fast-acting insulin is the clear one and it should be drawn first so it will not be contaminated by the long-acting insulin. The cloudy one, which is the long-acting insulin, should be also shaken first.
Study Guides:
Insulin: How to Give a Mixed Dose – UPMC
Steps for Preparing a Mixed Dose of Insulin – WebMD
3Anti-Hypertensive Drugs
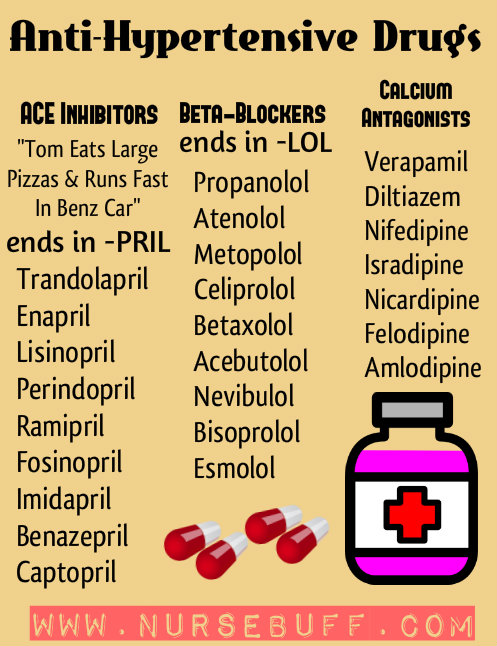
The top three most commonly prescribed anti-hypertensive drugs can be easily remembered through the mnemonic ABC – ACE inhibitors, Beta blockers and Calcium Antagonists.
ACE inhibitors end with “pril” like captopril, lisinopril and quinapril. On the other hand, beta blockers end with “olol” like atenolol, metoprolol and propranolol. Calcium antagonists end with “pine” like nifedipine, amlodipine and nircardipine. However, there are two calcium antagonists that don’t end in “pine” – diltiazem and verapamil.
Study Guides:
Medications for treating hypertension – Harvard Health Publications
4Antitussives, Expectorants and Mucolytics

There are three medications commonly prescribed to treat cough – antitussives, expectorants and mucolytics.
Antitussives work by reducing the urge to cough which is beneficial for non-productive coughs. Expectorants, on the other hand, irritate and stimulate the mucus membranes to induce the coughing reflex thereby facilitating the release of sputum from the respiratory tract. Mucolytics work more on breaking the links in the formation of phlegm so it would be easier to expel out of the lungs.
Study Guides:
Antitussives, Expectorants and Mucolytics – PharmacyInformatics
5Aldactone

Spironolactone or aldactone is a potassium-sparing diuretic that gets rid of sodium and water in the circulatory system while saving potassium in the blood. It blocks aldosterone in the kidney which is responsible in regulating the salt and water balance in the body. In using spironolactone, you should watch out for headache, diarrhea, hyperkalemia, electrolyte imbalance, fatigue and GI disturbances.
Study Guides:
6Nitroglycerin

Nitroglycerin primarily relaxes the vascular smooth muscle to decrease blood pressure and maintain an effective coronary perfusion pressure. It provides symptomatic relief for angina.
For quick relief, nitroglycerin as sublingual tablets and translingual sprays are recommended. For slow or controlled-release dosages, patches, ointments and sustained-release tablets should be used.
Study Guides:
7Anti-Retrovirals

Anti-Retrovirals work by terminating viral replication, blocking DNA activity and preventing the maturation of the retrovirus. These drugs also search for viruses and retroviruses that take different forms to escape the efficacy of standard anti-viral agents. Side-effects of using anti-retrovirals include rashes, headache and GI upset.
Study Guides:
8Steroids

Steroids or corticosteroids function in the same way as the body’s natural cortisol. They can decrease inflammation and reduce the immune system’s activity.
This is why the drugs are commonly prescribed to treat conditions and diseases that involve inflammation. They come in several forms and can be given by mouth, injected to a vein or into a muscle.
9Beta Blockers
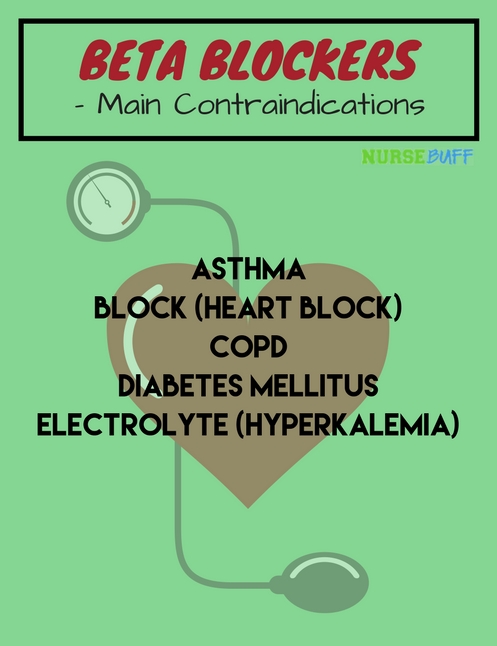
Beta blockers or beta-adrenergic blocking agents are primarily prescribed to lower blood pressure. They can also block the effects of epinephrine or adrenaline.
When a person takes a beta blocker, his heart will beat slower and with less force. The drug can also open up the blood vessels to enhance blood flow.
10Lithium

Lithium is frequently used in the treatment of certain cases of major depressive disorder where patients don’t respond well with other antidepressants. It is also the drug of choice for bipolar disorder.
Also Read:
Nursing Mnemonics & Tricks (Med-Surg Nursing)
Nursing Mnemonics & Tricks (Obstetrics and Newborn Care)
Nursing Mnemonics & Tricks (Diagnostics)
Nursing Mnemonics & Tricks (Assessment and Nursing Skills)



















