The challenging part of being a nurse doesn’t start when you get hired. It actually begins in nursing school. You’ll have to endure grueling lectures, stressful homework, and unpredictable tests and exams if you want to be a part of the profession.
Fortunately, there are plenty of nursing mnemonics that you can use in studying your lessons. Here are 25 of them.
1Abnormal Posturing
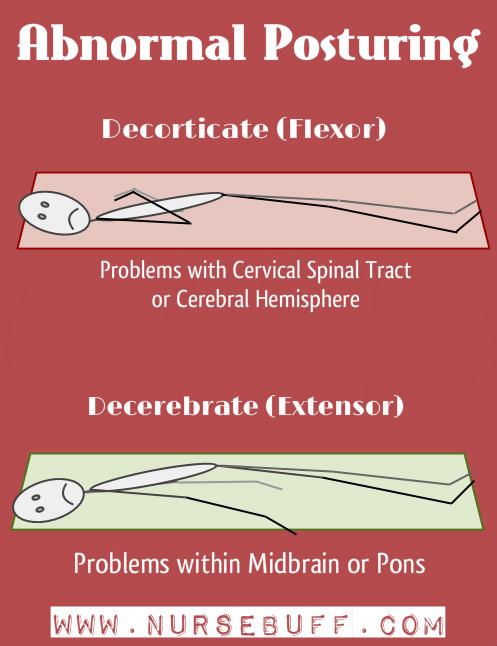
Decorticate posturing is the abnormal flexion of the body. It usually happens when there are problems in the cervical spinal tract or the cerebral hemisphere part of the brain.
To remember this posture, simply keep the word “flexor” in mind as patients with decorticate posture will have arms bend inwards to the chest.
Decerebrate posture, on the other hand, is the abnormal extension of the upper extremities. It typically happens in response to external stimuli.
It is often associated with problems within the midbrain or pons. It’s characterized by the extension of the arms and legs while the head is arched backward.
Study Guides:
What Causes Posture Abnormal? 12 Possible Conditions – Healthline
Abnormal Posturing and Potential Causes – Disabled World
2Anorexia Nervosa

Anorexia Nervosa is a type of eating disorder where the patient has this fear of gaining weight and intense desire to be thin. This often results in food restriction which compromises the patient’s overall health.
3Angina Pectoris

Angina pectoris is the medical term for chest pain. It typically happens when the heart doesn’t receive enough blood. In most cases, it’s due to problems with the heart’s arteries. They are either blocked or narrowed.
Emotional distress, exertion, eating, and extreme temperatures can trigger angina pectoris.
4Complications of Birth Control Pills
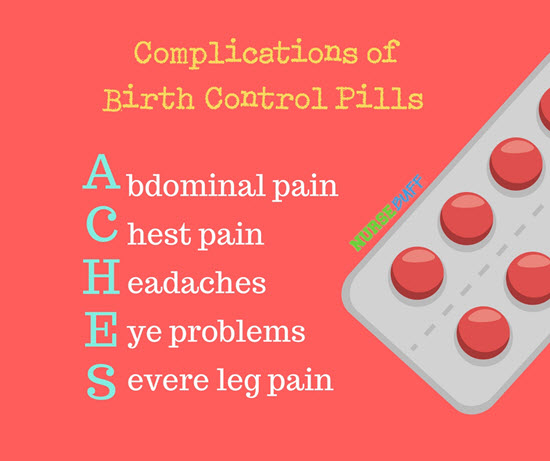
Birth control pills are taken by women of reproductive years to prevent pregnancy. They are around 99% effective if taken properly and as directed.
Now, although birth control pills are effective, it doesn’t mean that they are completely safe. If your patients are taking contraceptive pills, make sure to watch out for their common complications, like abdominal and chest pain, headaches, eye problems, and severe leg pain.
5Cholelithiasis Risk Factors

Cholelithiasis is the formation or presence of stones in the gallbladder. It’s classified according to what makes the stones.
Cholesterol gallstones are the most common type. They typically develop when the liver excretes way too much cholesterol than what the bile can dissolve. Bilirubin gallstones, on the other hand, happens when there’s excessive bilirubin.
The least frequent type of gallstone forms when there’s a problem in the emptying of the gallbladder.
Now, although there are several classifications, the risk factors for the condition apply to all types. This includes being a female, fertility, being fat, and being 40 years old and above.
6Cholinergic crisis

Cholinergic crisis happens when there’s too much acetylcholine. As a result, many organs and glands of the body, including the parasympathetic nervous system, get overstimulated. Symptoms to watch out for includes salivation, lacrimation, urination, and defecation. It’s an emergency and prompt treatment is necessary to control the patient’s airway.
7Compartment Syndrome

Compartment syndrome happens when pressure builds up, preventing nourishment and oxygen from reaching the muscles. This can result in nerve and tissue damage, muscles loss, amputation, and even kidney damage.
Now, before any of those things happen to your patient, watch out for the following signs of Compartment syndrome.
8Congestive Heart Failure

With left-sided CHF, the left ventricle fails to pump enough blood to the body. The fluid builds up in the lungs, causing difficulty breathing and other symptoms related to respiration.
Right-sided CHF, meanwhile, happens when the heart fails to pump enough blood to the lungs. As a result, the fluid accumulates in the lower extremities and other vital organs.
9Cor Pulmonale

Cor pulmonale refers to the enlargement or change in the structure and function of the heart’s right ventricle. Its most common cause is the increased blood pressure in the arteries of the lungs or pulmonary hypertension.
In addition to that, cor pulmonale can also happen as a result of COPD, cystic fibrosis, scleroderma, and obstructive sleep apnea.
See Also: 50 Nursing Mnemonics and Acronyms You Need to Know Now
10Dumping syndrome

Dumping syndrome relates to the group of symptoms that occur after eating. It particularly happens to patients who have undergone surgeries to remove parts of or all of the stomach.
Dumping syndrome is also called rapid gastric emptying. Dizziness, abdominal cramping, tachycardia, epigastric fullness, diaphoresis, and weakness can happen 15 to 13 minutes after eating.
11Epiglottitis
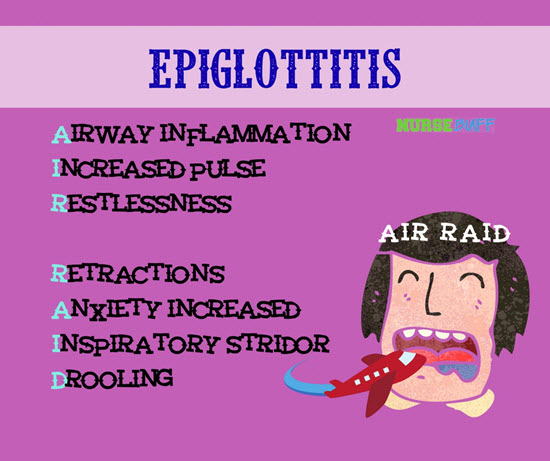
Epiglottitis is the inflammation of the epiglottis or the flap at the base of your tongue. It’s what keeps food from getting into your airway.
Most of the time, epiglottitis is caused by bacterial infection. The most common strain is Hib or Haemophilus influenzae type b. Its symptoms can develop quickly and may lead to serious complications if proper intervention is not given quickly.
12Episiotomy Assessment
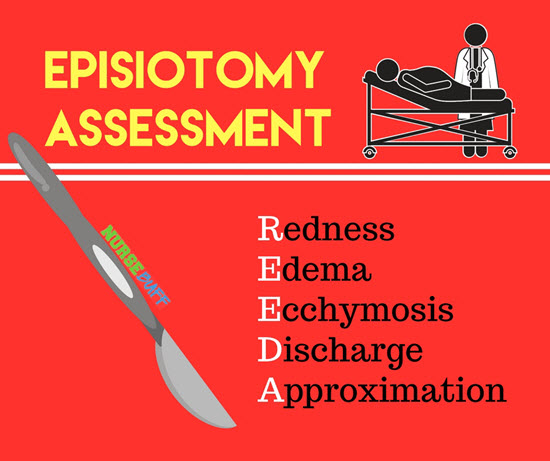
Episiotomy typically heals in two to three weeks. By such time, the stitches used for the procedure should have dissolved on their own.
When assessing a woman’s episiotomy, remember REEDA. Check for the presence of redness, edema, ecchymosis, discharge, and approximation. A little pain is normal after a week.
13Causes of Heart Murmur
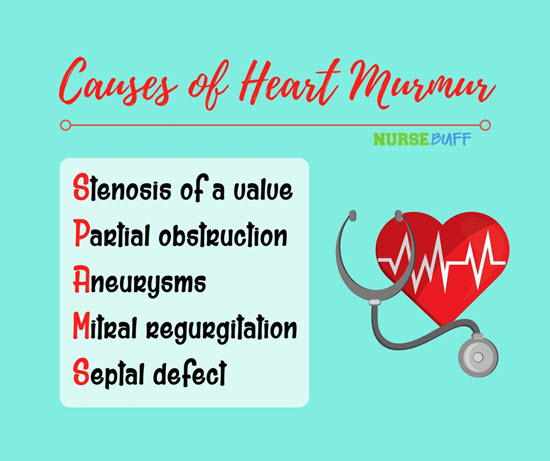
Heart murmurs can develop later in life or be present right at birth. They can indicate a potential problem with the heart, like stenosis of a valve, partial obstruction, aneurysms, mitral regurgitation or a septal defect.
Some heart murmurs are harmless and don’t require immediate treatment. However, if there are other signs and symptoms, follow-up tests may be necessary to check the heart’s true condition.
14Head Injury

In the first 24 hours after a head injury, a person should be closely observed for signs and symptoms that may indicate severe brain injury.
Assess the level of consciousness and determine if there is drowsiness, confusion or difficulty in arousing the patient. Seizures, visual problems, and unequal dilation or constriction of pupils should also be noted.
Bleeding or water drainage from the nose or ears and projectile vomiting are also classic symptoms of serious brain injury. Symptoms related to paralysis, like slurred speech and loss of sensation in certain extremities, should be checked, too.
Study Guides:
Severe Head Injury – NHS
Traumatic Brain Injury – Alzheimer’s Association
15Hypocalcemia Symptoms

Hypocalcemia is the presence of low calcium levels in the blood. Mildly low levels don’t usually show any symptoms. For excessively low levels, however, convulsions, arrhythmias, tetany, spasms, and stridor can develop. Treatment is usually with IV calcium.
16Hypoglycemia

Hypoglycemia is a condition characterized by abnormally low glucose levels in the blood. It usually results from insufficient intake of food, too much exercise, and excessive insulin administration.
Immediate symptoms of hypoglycemia include cool clammy skin, anxiousness, excessive sweating, confusion, blurred or double vision, and irritability. The onset of hypoglycemia is rapid at around 1-3 hours.
Study Guides:
Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Glucose) – American Diabetes Association
Hypoglycemia Definition – Mayo Clinic
17Hypoglycemia vs Hyperglycemia
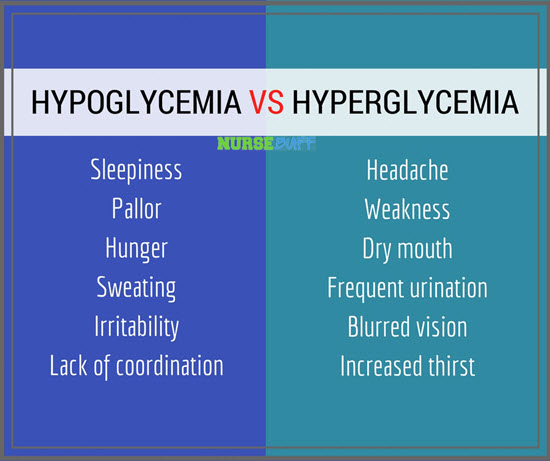
Hyperglycemia happens when a patient accumulates too much sugar in his bloodstream. It can be due to an illness, infection, eating too much, stress or not taking enough insulin.
Hypoglycemia, on the other hand, can happen to patients who eat late, don’t eat enough food, exercise too much or drink alcohol without eating anything. If a patient is taking insulin, he can also experience hypoglycemia if too much insulin is used.
When assessing a patient, carefully checking his symptoms can give you a hint of his blood sugar level. Verify by performing appropriate tests.
18Hypoxia
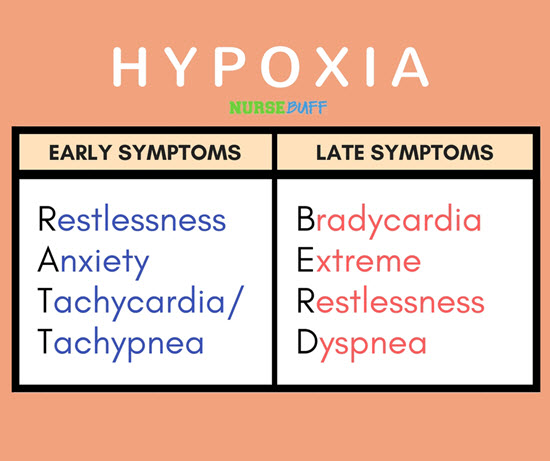
Hypoxia refers to the inadequate oxygen supply reaching the tissues. It can happen when there’s damage to the lungs due to trauma or lung diseases.
Hypoxia is a dangerous condition. Without enough oxygen, the brain can quickly cease to function. As a nurse, this makes it important that you know how to recognize early signs of hypoxia so you can act right away.
19Increased ICP vs Shock
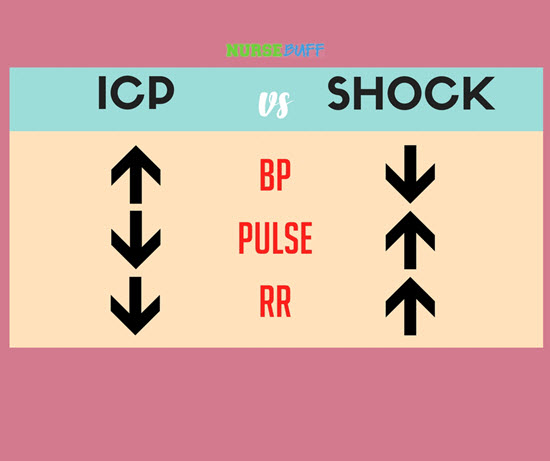
Increased intracranial pressure is typically caused by a rise in the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid or an increase in pressure within the brain. It’s a serious medical issue that requires prompt treatment.
Shock is also a medical emergency where a patient loses more than one-fifth of his fluid supply or blood. With severe fluid loss, the heart may not be able to pump sufficient blood to the body.
When it comes to symptoms, those two conditions are the exact opposite. In increased ICP, a patient’s blood pressure increases while his pulse and respiratory rates decrease. In shock, the patient has a decreased blood pressure while his pulse and respiratory rates increase to compensate.
20Treatment for myocardial infarction
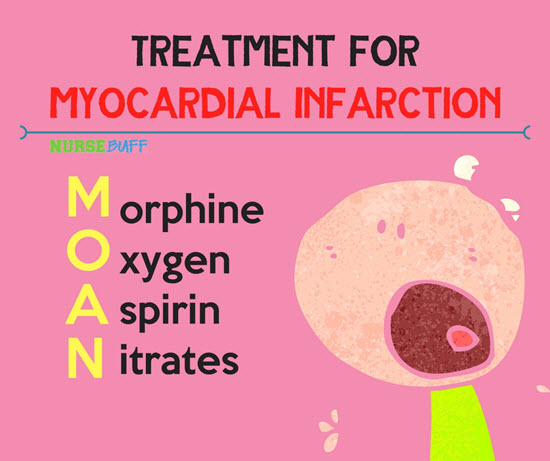
Treatment for myocardial infarction or heart attack should be given quickly to limit the damage to the heart muscle. If the medications are delayed, the more damage can happen and the less effective they’ll be.
21Risk Factors for Osteoporosis

Osteoporosis is a type of bone disease where the bones become extremely weak to the point that they’ll easily break with daily activities. You are at an increased risk of developing it if you are drinking alcohol, smoking or under corticosteroid treatment. Low calcium and estrogen levels in the blood can also cause osteoporosis.
22Cardinal Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease
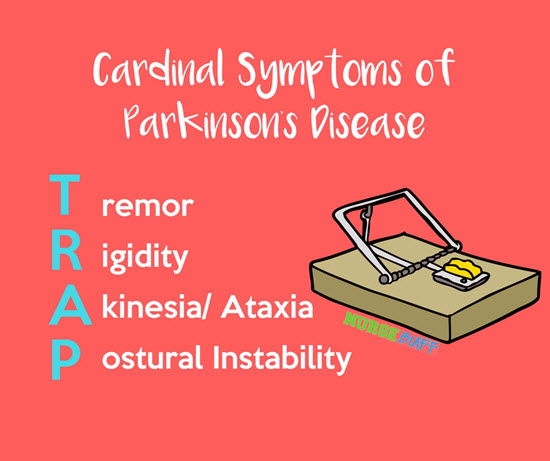
Parkinson’s disease develops slowly. The signs you’ll likely observe include tremors, rigidity, akinesia/ataxia, and postural instability. They can get worse as the disease progresses. They can even affect the patient’s quality of life.
23Pneumothorax Symptoms

Pneumothorax is the collection of air in a patient’s chest cavity which causes the lungs to collapse. It can happen because of a trauma or injury or an underlying lung disease.
Assessment will reveal decreased or absent breath sounds with auscultation. It can be confirmed by performing a chest X-ray.
For the initial assessment, check for pleuritic pain, tracheal deviation, hyper-resonance, sudden onset of reduced breath sounds, and absent fremitus if you suspect pneumothorax.
24Postpartum Assessment
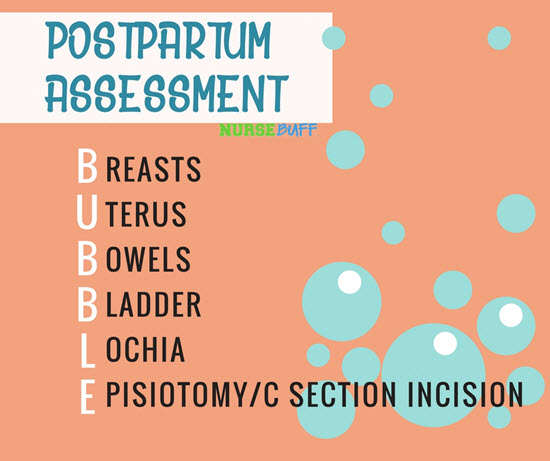
Postpartum assessments are carried out to ensure that the patient is coping well and that there are no complications after delivery. The frequency of assessment can vary depending on hospital policy.
When assessing postpartum patients, check the breasts, uterus, bowels, bladder, lochia, and episiotomy/incision along with their vital signs.
25Danger Signs of Pregnancy

A lot of women go through pregnancy with a few minor discomforts. As a nurse, you need to know how to differentiate those minor discomforts from the danger signs of pregnancy. Failure to recognize these danger signs can compromise both mother and child.
26Severe Preeclampsia
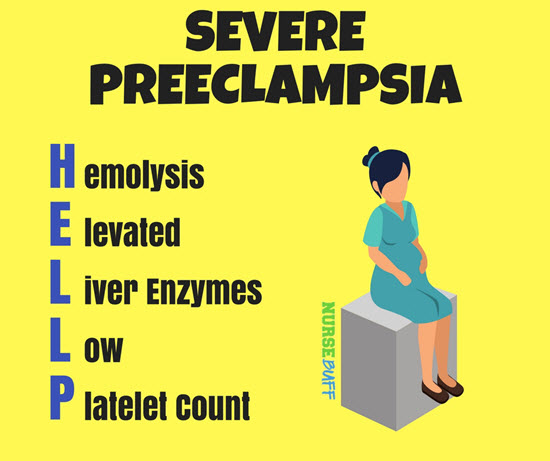
If severe preeclampsia is not treated right away, the mother can be at an increased risk of developing renal or liver failure. She’ll be at risk of cardiovascular problems, too.
It’s also possible for her to experience eclampsia where seizures occur. Once that happens, the placenta may not get enough blood which means the baby won’t get enough oxygen and food, too. As a result, the baby can have a low birth weight.
Also Read:
Nursing Mnemonics & Tricks (Pharmacology)
Nursing Mnemonics & Tricks (Obstetrics and Newborn Care)
Nursing Mnemonics & Tricks (Diagnostics)
Nursing Mnemonics & Tricks (Assessment and Nursing Skills)