1. Amniotic Fluid.

The amniotic fluid is a clear, yellowish liquid that surrounds the fetus during pregnancy. It is contained in the amniotic sac and helps the developing baby move in the womb, encourages proper bone growth, helps the lungs develop properly, helps keep a relatively constant temperature around the fetus and protects the fetus from outside injury by cushioning sudden blows or movements.
Also Read: 10 Nursing Mnemonics & Tricks (Obstetrics &Newborn Care)
Excessive amniotic fluid, which is known as oligohydramnios, is a condition that may occur in late pregnancies, placental dysfunction, ruptured membranes or fetal abnormalities.
The most common tests for diagnosing the rupture of membranes are the Nitrazine test and the pH test. The Nitrazine test involves placing small amounts of vaginal fluid onto paper strips prepared with Nitrazine dye. A chemical reaction occurs and the strips change color, indicating the pH of the vaginal fluid. If the color shows the pH is greater than 6.5, it’s likely the membranes have ruptured.
2. Cord Compression.

Fetal distress occurs when the baby’s oxygen supply is compromised in utero — either during pregnancy or during labor. The distress may be caused by factors such as maternal illness, placental abruption, umbilical cord compression, fetal infection, or simply because the mother is in a position that puts pressure on major blood vessels, depriving the baby of oxygen. The best care for cord compression is to place the mother in a Trendelenburg position, so as to remove pressure of the presenting part off the cord.
3. Ectopic Pregnancy.

Ectopic pregnancies occur when a fertilized egg is not able to attach to the uterus. Common causes of ectopic pregnancies include inflammation and scarring of the fallopian tubes due to a previous medical condition or surgery, hormonal factors, genetic abnormalities, birth defects, and medical conditions that affect the shape and condition of the fallopian tubes and reproductive organs.
4. Folic Acid (Vitamin B9).

Folic acid helps the body make healthy new cells. It is especially important for women who are pregnant to prevent major birth defects. Folic acid is usually found in leafy green vegetables, fruits, dried beans, peas, nuts, enriched breads, cereals and other grain products.
5. FHR Patterns.
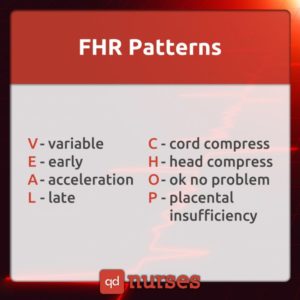
Assessment of fetal well-being during labor involves electronic fetal heart rate monitoring. Detection of fetal compromise does not guarantee a riskless labor, but it can help with fetal monitoring.
Early decelerations are seen when the baby’s head is compressed. This often happens during the later stages of labor as the baby is descending through the birth canal.
Late decelerations, however, do not begin until the peak of a contraction or thereafter. They usually signify a reduced oxygen supply to the baby.
Variable decelerations do not look like late or early decelerations. They are generally irregular, often jagged dips in the fetal heart rate that look more dramatic than late decelerations.
6. Gynecoid Pelvis.

They are the gynecoid, most common female pelvis shape; the android, the most common male shape; the anthropoid, a long pelvis; and a platypelloid or flat-shaped pelvis. A gynecoid pelvis is oval at the inlet, has a generous capacity and wide subpubic arch. It is more delicate, wider than and not as high as the male pelvis.
7. HIV-Positive Infants.

8. Lightening.

Lightening usually occurs a few weeks or a few hours prior to labor. It means the baby is settling or lowering into the pelvis just before labor. Lightening is also part of the body’s preparation for labor.
9. Movements of Delivery.

The movements of delivery refer to the changes in position of fetal head during its passage through the birth canal.
Engagement refers to passage of the widest diameter of the presenting part to a level below the pelvic inlet plane.
Descent is when the fetal head is pushed deep into the pelvis sideways.
Flexion refers to the flexing of the chin to come into contact with the infant’s sternum. The occiput position allows the occipital bone in the back of the head to lead the way.
Internal rotation usually depends on the infant’s position and the way the head rotates to accommodate itself to the changes in the pelvic diameters. Engagement is when the presenting part is at the level of the ischial spine.
The external rotation allows the widest diameter of the shoulders to be delivered from the longer anteroposterior diameter of the pelvic outlet.
Extension is when the infant’s chin lifts up or extends to allow the head to be delivered. Expulsion involves the delivery of the anterior shoulder, then the posterior shoulder, followed by the rest of the infant’s body.
10. Pre-eclampsia.

Pre-eclampsia in pregnant women is marked by high blood pressure and a high level of protein in the urine. Signs and symptoms usually include swelling, proteinuria, increased blood pressure, rapid weight gain, abdominal pain, severe headaches, change in reflexes, reduced or no urine output, dizziness, excessive vomiting, nausea, and vision changes.
11. Prolapsed Cord.

A prolapsed cord is an obstetric emergency in which the umbilical cord passes through the cervix at the same time as or earlier than the fetal presenting part. This may lead to fetal hypoxia, and if not rapidly treated, may lead to long-term disability or even death.
12. TORCHS Syndrome.

TORCHS Syndrome is an infection caused by a group of infectious agents which has been transmitted from the mother through the placenta. Infections include toxoplasmosis, rubella, cytomegalovirus, herpes virus, syphillis and hepatitis.
Symptoms include enlarged liver, enlarged spleen, fetal malformations, jaundice, chorioretinitis, low blood platelet level, cataracts, hearing loss, mental retardation, hemorrhagic skin spots, and fetal death.
13. Transesophageal Fistula.

Transesophageal fistula is a congenital condition in which an abnormal channel connects the trachea to the esophagus. Food and saliva get into the trachea and lungs through the abnormal channel, which may cause choking, coughing, cyanosis, or lung infections such as pneumonia.
14. Umbilical Cord.

The umbilical cord connects the baby in the womb to its mother. Oxygen and nutrients from the mother’s bloodstream pass into the baby’s bloodstream through the umbilical cord.
The vein carries oxygen-rich blood and nutrients from the mother to the baby. The arteries, on the other hand, return deoxygenated blood and waste products, like carbon dioxide, from the baby back to the placenta.
See More:
1. Nursing Flashcards (Communicable Diseases)
2. Nursing Flashcards (Diagnostics and Lab Procedures)
3. Nursing Flashcards (Fundamentals of Nursing)
4. Nursing Flashcards (Medical-Surgical Nursing)
5. Nursing Flashcards (Nutrition)
6. Nursing Flashcards (NCLEX Tips/Psychiatric Nursing)
7. Nursing Flashcards (Pediatric Nursing)
8. Nursing Flashcards (Pharmacology)



















