Do you know that there are many old medicine remedies lately being proven harmful for human consumption?
Thanks to the hardwork of researchers, the world became aware of the harmful medications typically used in healthcare in the early times. Your parents and grandparents may have taken these antiquated medications before they were pulled out from the market.
Let us take a look at these old medications. Do you know any of them?
1. Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT)

Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane or simply know as DDT is a potent insecticide. It was first discovered in 1874 and widely used during the 1940s. At first, it was used in aerial spraying to control outbreaks of dengue fever and malaria. Later on, it was used for treatment of lice infestation.
As lice infestation is rampant among children, nurses during this time sprayed children with DDT powder. The spray looked like a manual balloon air pump. Soldiers were also sprayed with the powder to prevent the spread of typhus-carrying lice during World War II.
Soon enough, the US Government banned the use of DDT in 1970s. DDT was found to be highly toxic for humans. It was also proven teratogenic and carcinogenic in clinical trials.
Also Read: 7 Vintage Medical Equipment Nurses Used in the Past
2. Paregoric

Paregoric is a camphorated tincture of opium. It is one of the most popular old medicine remedies used for centuries. It was first invented in the early 18th century for the treatment of asthma and was otherwise known as Elixir Asthmaticum.
By the 19th century, physicians began prescribing it to babies and children for the treatment of diarrhea, cough and teething discomforts. Nurses administered it by drops or teaspoons and instructed mothers on proper usage at home.
From the 1900s to the 1960s, paregoric could be purchased readily in apothecaries and pharmacies. It was a common item in every household’s drug cabinet during that time.
Then, the US government began controlling the sales of paregoric in the 1970s when the addicting potential of narcotics was clinically proven.
3. Merbromin
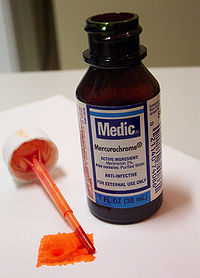
Merbromin is widely known as Mercurochrome. It’s a topical antiseptic commonly used for the treatment of minor wounds, cut, burns and scrapes.
In 1950s, merbromin was used for daily wound care of diabetic foot sores and ulcers. When applied to the skin, it produced a distinctive carmine red stain. The stain stayed on the skin for several weeks, even after repeated washes. The solution was also commonly used by nurses and midwives for antisepsis of umbilical cord in birthing facilities during this time.
Because of merbromin’s mercury content, the US Food and Drug Administration banned its use in 1998. It can potentially cause mercury poisoning especially when used in large amounts.
4. Candettes

Candettes are similar to cough lozenges. Based from their ad, it contained two undisclosed types of antibiotics and an anesthetic compound for immediate relief of sore throat. It became popular in the 1950s under Pfizer’s name.
Due to the success of candettes among consumers, more products under this trademark was produced like cough syrups, cough gels and cold tablets.
Candettes was later discontinued in the 1970s.
5. Heroin
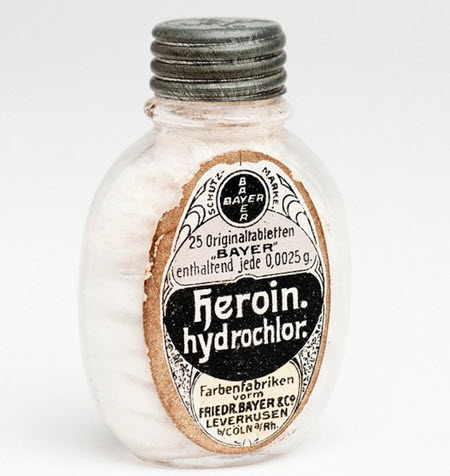

In 1898, Bayer commercially released Heroin, a concoction of diacetylmorphine. It was advertised for the treatment of cough and colds.
During the US Civil War, there was rampant use of morphine among injured soldiers. After the war, many soldiers became addicted to morphine which was later termed as “Soldier’s Disease”. When Heroin came out to the market, it became a potential solution for morphine addiction. In 1906, the American Medical Association recommended Heroin for medical use especially as a replacement for morphine.
Nurses in 1900s, under the prescription of hospital physicians, administered Heroin to patients recuperating from tuberculosis, bronchitis, pneumonia and other lung disorders.
In 1914, use of Heroin was controlled under the Harrison Narcotics Act.
6. Cocaine Toothache and Cough Drops

Cocaine has been widely used for the treatment of cough and colds since the 19th century. It became so popular that apothecaries would often buy cocaine drops in bulk and they would repackage them under their own name.
By 1950s, there were documented cases of cough syrup addiction. The US government investigated and discovered that most cough syrups contained cocaine. They began controlling usage of cocaine in medications by 1970s.
7. Delysid
Delysid is a popular brand name for Lysergic Acid Diethylamide or LSD. The drug compound was discovered in 1938 by a chemist named Albert Hoffman.
Hoffman accidentally ingested LSD and discovered its hallucinogenic properties. Since then, the drug became a subject of experimental studies for the treatment of various mental illnesses. Soon, Delysid was prescribed to patients with mental illnesses especially those committed in asylums.
Because of Delysid’s hallucinogenic properties, the drug became famous not for clinical treatments but for recreational usage. In 1980s, Delysid was pulled out for clinical use because of its addictive properties.
8. Dr. Nathan Tucker Asthma Specific
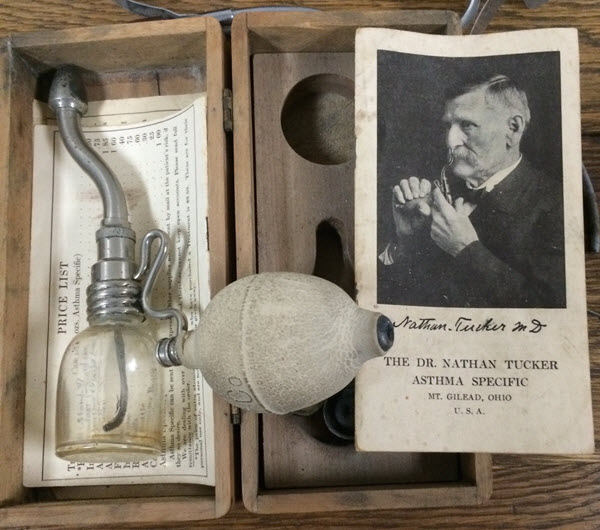

Dr. Nathan Tucker Asthma Specific is an early version of inhaler. The drug came with an inhaler-like device that vaporized accompanying liquid drug for immediate relief of asthma.
It became popular in the 1900s even though the components of the drug was unclear to the public. During that time, drugs were marketed without their components or generic names to protect the manufacturer’s supposedly secret formula.
When analysis was made on the remaining samples of the drug, it was discovered that it contained cocaine and atropine. This was the reason why it became addictive to patronizing users. The relief felt by its users was actually related to cocaine euphoria. The drug was discontinued during the implementation of narcotic drugs control.
Also Read: 15 Old Nursing Skills We Don’t Use Anymore
9. Mornidine

Mornidine was prescribed before to pregnant women suffering from hyperemesis gravidarum. For some pregnant women, morning sickness is so severe that they needed short hospital stays for hydration. Mornidine offered immediate relief for this problem as it worked in suppressing the “vomiting center” of the brain. It became popular in the 1950s.
In 1969, the US Food and Drug Administration banned the use of Mornidine. It was proven that the drug causes severe side effects in the liver, mainly hepatic lesions and hepatotoxicity.
10. Distaval
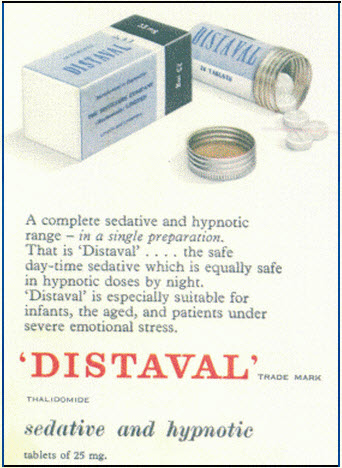
Distaval is the popular brand name for thalidomide. The drug came out in the 1950s which was marketed as a mild sedative and an effective drug for morning sickness. Chemie Grunethal, the drug’s manufacturer, claimed that the drug was safe for pregnancy.
The drug was used in over 40 countries. A few years later, women who took the drug gave birth to babies with multiple congenital defects. Some babies were born blind, deaf and with deformed limbs. In severe cases, babies are even born without vital organs.
Distaval was immediately discontinued in the market and the manufacturer was obliged to pay settlement fees to affected families. Around 5,000 survivors were still alive nowadays and some of them are still receiving a small amount of support from drug companies who sold the drug.
Do you know of other old and dangerous medicine remedies not included in this list? It’s amazing to see how far we’ve advanced in the field of medical research nowadays.
Share this informative article to your colleagues and fellow nurses. We bet even your non-nursing friends and family will find this post interesting!



















