Telehealth and telemedicine have enjoyed unprecedented growth in recent months, but even before then it was something patients were clamoring for. Of course, patients don’t always know the risks of untested procedures and practices, so healthcare providers have to carefully weigh the risks and rewards before implementing something they can’t easily take back.
But now that both healthcare providers and patients have seen what telehealth and telemedicine can do, these technologies are likely to continue to grow in both use and popularity.
What’s The Difference Between Telehealth And Telemedicine?
While these terms are often used interchangeably, they encompass completely different functions. Telehealth is the use of technology, including telecommunications and other forms of electronic information, to provide remote healthcare. These remote services can include patient monitoring via the use of equipment with transmitters, patient and staff education and training, hospital administrative meetings, and more.
Telemedicine, on the other hand, strictly applies to virtual medical services. This can include video conferences between a healthcare provider and a patient or more involved medical services that require specialized telemedicine tools.
The Growing Popularity Of Telemedicine

It’s no wonder telemedicine has become so popular. It allows patients to have uninterrupted access to healthcare providers, even when medical offices are inaccessible.
Telemedicine has long been a lifeline for remote and rural patients, but it is becoming more popular in places like nursing homes where patients might have mobility or chronic health issues that make it difficult to move them to a different facility for routine treatment.
Telemedicine also makes it easier to achieve patient compliance in rural and remote populations as well as in those with chronic health or mobility issues. Getting a patient to make routine checkups when there are barriers can be extremely difficult, especially when treatment proceeds as planned and works.
The better the treatment plan works, the less likely a patient is to see value in continuing, thinking they have been “cured” so why bother. Making these routine visits as easy as possible can help keep patients on track to recovery.
Telemedicine prevents unnecessary emergency room visits, increases accessibility of physicians to patients, decreases avoidable hospital readmissions, and promotes quality of life by making early interventions more accessible.
Why Telemedicine Is Going To Continue To Grow In Popularity
Currently, 60% of patients would prefer to have a telemedicine option to see their medical providers, but only 20% of doctors and 10% of hospitals have the necessary equipment to be able to provide those services to patients. Physicians are concerned about how to keep protected health data secure while also worrying about a potential increase in medical errors.
Patients who have already experienced telemedicine visits are overwhelmingly happy with the experience, though. The report:
- 66% improved access to care
- 52% greater satisfaction with treatment
- 45% better connection with their providers
Meanwhile, physicians who used telemedicine saw:
- 42% improvement in patient outcomes
- 32% better workflow
- 28% increase in connection with peers
Nurses Are The Key To Successful Long-Term Telemedicine Use
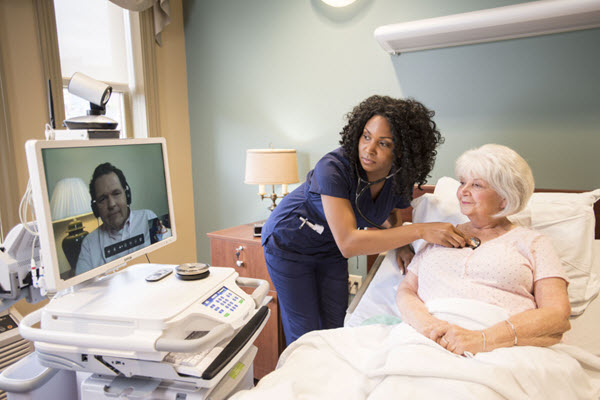

Telemedicine is not just video conferences between patients and their providers. In order for telemedicine to work well in the long term, more sophisticated technology will have to be used. Telemedicine carts are becoming more advanced, and they include equipment such as stethoscopes, dermoscopes, an HD camera, and an electrocardiogram for cardiac assessment. Of course, it takes a seasoned medical provider, such as a nurse, to be able to operate this equipment properly.
Nurses can help bridge the gap in areas where physicians are not easily accessible or in populations where traveling for medical care is burdensome. This equipment is especially helpful in skilled nursing and long-term care facilities where patients are more likely to have chronic conditions that need to be managed as well as limitations on mobility. Many routine assessments can be made with telemedicine carts with the help of nurses, providing patients with a higher level of care with more convenient access.
As telemedicine advances and more patients interact with it, medical providers will need to adapt to offer this service to those patients who want it and for whom it is appropriate.
Learn more about the differences between telehealth and telemedicine as well as how nurses will play a role in its growth from the infographic below.













![Are You Ready For An Online Nursing Program? [Infographic] online nursing program requirements and benefits](https://www.nursebuff.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/09/online-nursing-program-requirements-and-benefits2-100x70.jpg)