1. Airborne Diseases.

Diseases that are spread when droplets of pathogens are expelled into the air by coughing, sneezing or talking are called Airborne Diseases. These diseases usually require prolonged exposure to infection prior to occurrence, thus posing minimal threat to other people.
There are preventive measures such as wearing masks or maximizing ventilation to reduce risks of acquiring airborne diseases. It is preferred that patients who require airborne precautions are placed in an airborne infection isolation room (AIIR), which is a single-patient room that is equipped with special air handling and ventilation capacity that meets the American Institute of Architects/Facility Guidelines Institute (AIA/FGI) standards for AIIRs.
2. Contact Diseases.

Contact diseases are transmitted when an infected person has direct bodily contact with an uninfected person, and the microbe is passed from one to the other. Contact diseases can also be spread indirectly through the infected person’s environment or personal items.
Direct contact diseases include conditions such as anthrax, coronavirus, enterovirus, group A Streptococcus, Invasive group B Streptococcal (GBS), Haemophilus influenza, legionellosis, meningococcal disease, MERS-CoV, MRSA, plague, strep pneumoniae, and SARS. Other conditions include Conjunctivitis (Pink-eye), Creutzfeldt-Jacob (CJD), Erythema infectiosum (Fifth disease), Impetigo, Pediculosis (Head lice), Polio, Roseola, Rubella (German measles), Scabies, Tetanus, and Vesicular stomatitis (Hand, foot, and mouth disease).
3. Droplet Precautions.

Droplet precautions apply to patients who have conditions that may be transmitted by droplet route. These are usually respiratory viruses such as influenza, parainfluenza virus, adenovirus, respiratory syncytial virus, human metapneumovirus, bordetella pertussis, Neisseria meningitides, and group A streptococcus.
4. Pertussis.

Pertussis is a highly contagious bacterial disease that causes uncontrollable and violent coughing. It is caused by the Bordetella pertussis or Bordetella parapertussis bacteria. Symptoms usually develop about a week after exposure to the bacteria. They include severe episodes of coughing, vomiting, loss of consciousness caused by coughing spells, runny nose, slight fever, and diarrhea.
5. Skin Infections.
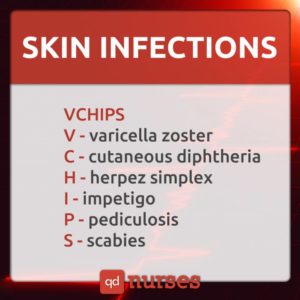
Infections of the skin may be caused by a wide variety of microorganisms. In some severe cases, the infection may spread beyond the skin and into the bloodstream. Symptoms include redness of the skin, cellulitis, swelling, blisters, and lesions among others.
See More:
1. Nursing Flashcards (NCLEX Tips/Psychiatric Nursing)
2. Nursing Flashcards (Diagnostics and Lab Procedures)
3. Nursing Flashcards (Fundamentals of Nursing)
4. Nursing Flashcards (Medical-Surgical Nursing)
5. Nursing Flashcards (Nutrition)
6. Nursing Flashcards (Obstetrics and Newborn Care)
7. Nursing Flashcards (Pediatric Nursing)
8. Nursing Flashcards (Pharmacology)


















