Studying Fluid and Electrolytes is ridiculously hard and there’s no denying that. Apart from memorizing lab values as well as the signs and symptoms of having electrolyte imbalances, you also have to know how to interpret the values and create a nursing care plan for your patient’s condition. As a student, those things can really overwhelm you.
Instead of feeling anxious and scared, one of the best things you can do to master Fluid and Electrolytes is to commit to memorizing. And to help you out, here are some nursing mnemonics and acronyms you’ll find handy.
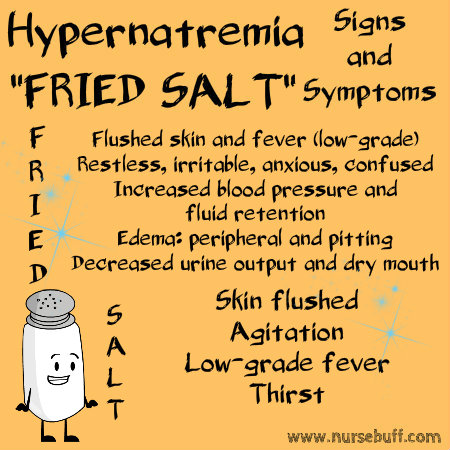
Hypernatremia Signs and Symptoms — “FRIED SALT”
Hypernatremia refers to a condition wherein the serum or plasma sodium is greater than 145 mEq/L. It is often due to water that is excessively lost through the gastrointestinal tract, skin or urine.
Hyponatremia Signs and Symptoms – “SALT LOSS”

Hyponatremia happens when there’s a lower level of sodium in the blood than normal. This can be due to an inadequate intake of sodium or excessive water intake that lowers the concentration of sodium.
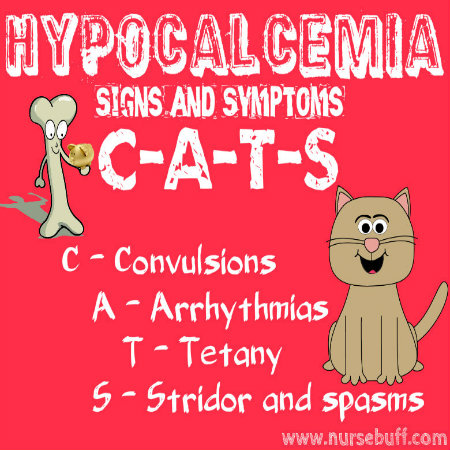
Hypocalcemia Signs and Symptoms — “CATS”
Hypocalcemia occurs when the level of calcium in the body becomes abnormally low. It may be the result of low calcium production or insufficient calcium circulation in the body.
Hypercalcemia Causes – “CHIMPAN”

Hypercalcemia Signs and Symptoms – “BACK ME”

Hypercalcemia is when the level of calcium in the blood is way above normal. If hypercalcemia is mild, its signs and symptoms might not show up that much. In severe cases, however, it can greatly affect the kidneys, digestive system, brain, heart, and bones.
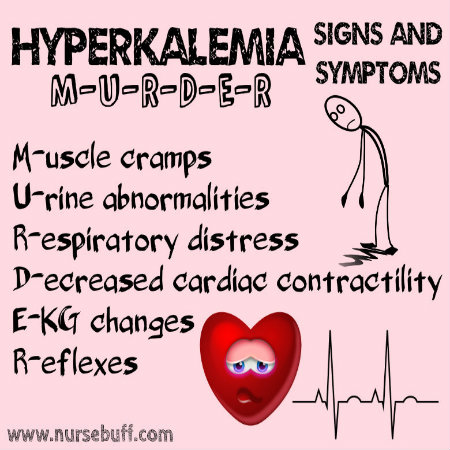
Hyperkalemia Signs and Symptoms — “MURDER”
Hyperkalemia, or high potassium level in the blood, usually occurs when inefficient kidneys fail to remove potassium from the body or if the cells in the body release too much potassium. Excessive consumption of potassium may also lead to hyperkalemia, especially if the kidney function is compromised.
Signs and symptoms of hyperkalemia include muscle cramps that progress to weakness; urine abnormalities like oliguria or anuria; respiratory distress; decreased cardiac contractility; EKG changes; and abnormalities in reflexes such as hyperflexia or areflexia. These can easily be remembered using the acronym MURDER.
Hypokalemia Signs and Symptoms — “A SIC WALT”
Low potassium level or hypokalemia is usually caused by kidney disease, antibiotics, diarrhea or vomiting, eating disorders, or sweating, among others.
Signs and symptoms of hypokalemia can be remembered using the acronyms A SIC WALT: Alkalosis, Shallow Respirations, Irritability, Confusion and drowsiness, Weakness and fatigue, Arrhythmias like tachycardia or bradycardia, Lethargy, and Thready pulse. There may also be decreased intestinal mobility, vomiting, and ileus. Try to picture your patient, Mr. Walt, saying “I am A SIC WALT.”