Medical mnemonics are helpful study aids for nursing examinations like NCLEX. Many students use them in remembering complex nursing concepts. Fortunately, there are plenty of eye-catching nursing mnemonics around that you can use in studying especially for NCLEX.
Here are some of the popular mnemonics among nursing students. Can you remember them all?
Note: We took the most popular pins on Pinterest and put them together in this list. If you want to know more about any particular pin, just click on it to get to the original pin on Pinterest and the source website.
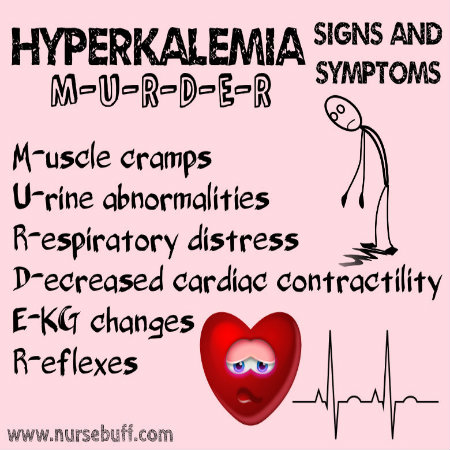
1. Hyperkalemia
Hyperkalemia refers to high potassium level in the blood. This is the result of kidneys releasing too much potassium or failing to remove potassium from the body. If the kidney is already compromised and potassium is excessively consumed, hyperkalemia can also occur.
Ironically, the acronym for the signs and symptoms of hyperkalemia are M-U-R-D-E-R.
Also Read: Nursing Mnemonics and Acronyms – (Respiratory, Endocrine and Nervous System)
2. Aldactone
Aldactone, also known as spironolactone, is a potassium-sparing diuretic. It works by blocking the effects of aldosterone in the body. Through the inhibition of aldosterone, the kidney will be able to excrete excess fluid and sodium in the body without affecting potassium levels.
Potassium-sparing diuretic is essential in maintaining normal serum potassium levels. Other diuretics don’t spare potassium during diuresis which may lead to hypokalemia.
3. Acidosis – Alkalosis
Acidosis occurs when an excess of acid in the blood causes the pH to fall below 7.35. In contrast, alkalosis occurs when an excess of base in the blood causes the pH to rise above 7.45. Easily recall what’s up and what’s down with this mnemonic.
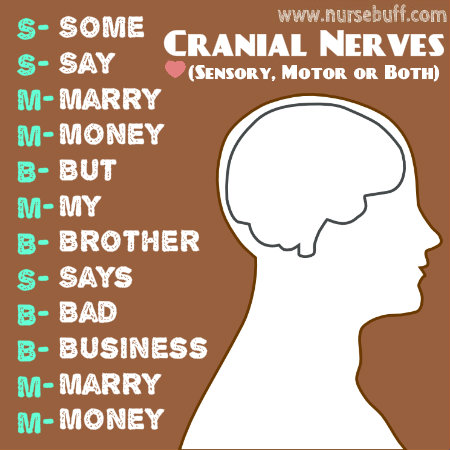
4. Cranial Nerves (Sensory, Motor or Both)
Cranial nerve functions are sensory, motor, or both. The list of cranial nerve functions is somewhat long but you can easily remember it with this funny mnemonic: Some say marry money but my brother says bad business marry money.
Also Read: 25 Psychiatric Nursing Mnemonics and Tricks
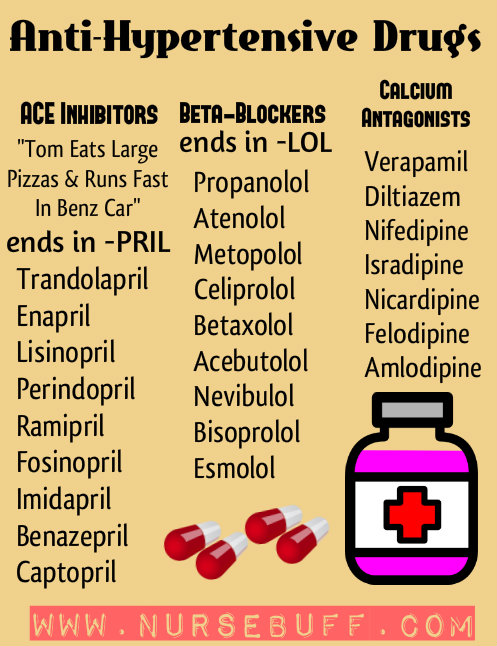
5. Antihypertensive Drugs
There are three main types of anti-hypertensive medication – ACE Inhibitors, Beta Blockers and Calcium Antagonists.
ACE Inhibitors work by inhibiting the enzyme angiotensin II to decrease peripheral vascular resistance. This group of drugs ends in “pril” like captopril, enalapril and benzopril.
Beta blockers, also known as beta-adrenergic blockers, work by blocking adrenaline and noradrenaline at the adrenergic beta receptors to weaken the effects of stress hormones in the elevation of blood pressure. This group of drugs end in olol like atenolol, nadolol and propranolol.
Calcium antagonists, also known as calcium channel blockers, disrupt the movement of calcium in calcium channels to reduce blood pressure. These drugs usually end in “dipine” like nifedipine, nicardipine and amlodipine. Other calcium antagonists that do not end in dipine include verapamil, gallopamil, fendiline and diltiazem.
6. Antitussive, Expectorants and Mucolytics
Antitussives, expectorants and mucolytics are the drugs used in the management of respiratory disorders. They work on the phlegm production and coughing mechanism of the body.
Antitussive is effective in relieving dry cough as it reduces the activity of the cough centre in the brain. Examples include dextromethorphan, codeine, benzonatate and noscapine.
Expectorants irritate the mucus membrane to facilitate easy expectoration of secretions.
Guaifenesin is an example of expectorants.
Mucolytics work by enhancing the hydration of secretions thereby loosening mucus plugs for easy expectoration. Examples include acetylcysteine and erdosteine.
Also Read: Nursing Mnemonics and Tricks – Pharmacology
7. Asthma Mnemonic
Management of asthma can be easily remembered with the mnemonic ASTHMA – adrenergic, steroids, theophylline, hydration, mask for oxygen therapy and antibiotics.
Adrenergic, steroids and theophylline work as bronchodilators whereairways are made larger to allow easier passage of air into the lungs. Hydration is essential to loosen secretions in the lungs for easy expectoration. Oxygen support is also given to ensure adequate oxygenation while other therapies work on improving airway passage. And lastly, antibiotics are also given to resolve beginning infection that may result from the inflammation of airways.
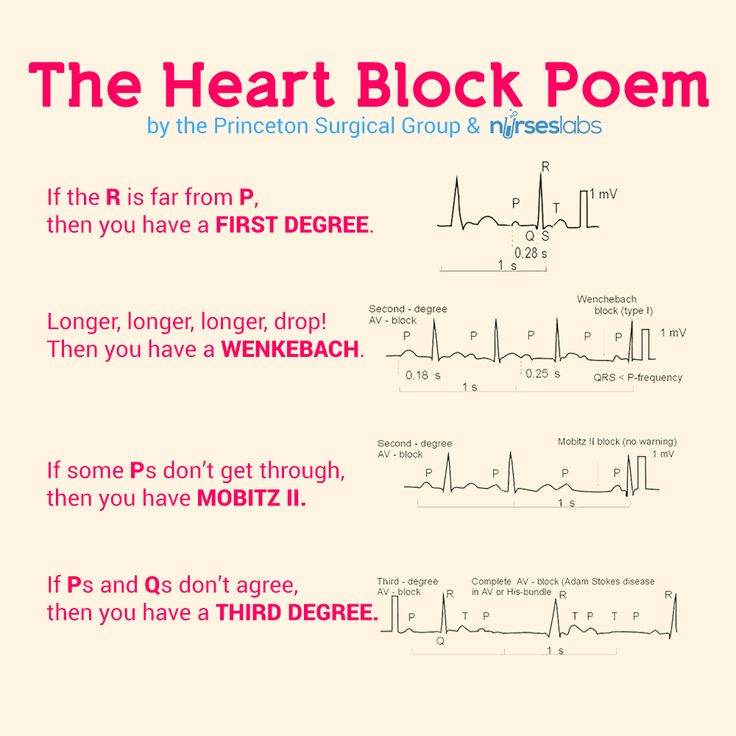
8. Cardiac Arythmias
There are four heart blocks discussed in this mnemonic – first degree, second degree type 1 or also known as Wenkebach, second degree type 2 or also known as Mobitz II and third degree.
In first degree heart block, there is a slow passage of electrical impulses in the conduction system but they eventually reach the ventricles. Most of the time, there is no sign or symptom for this problem.
In second degree type 1 heart block or also known as Wenkebach, the electrical impulses are delayed with each heartbeat until a beat fails to reach the ventricles. Patients with this type of heart block commonly experience dizziness and in worst cases, syncope.
In second degree type 2 heart block or also known as Mobitz II, some of the electrical impulses of the heart are unable to reach the ventricles completely. This condition usually requires pacemaker and may progress to third degree heart block.
In third degree heart block, also known as complete heart block, all electrical impulses from the atria are unable to reach the ventricles. Patients with third degree heart block often feel lightheadedness and fatigue.
9. RLQ Pain – APPENDICITIS
Right lower quadrant pain can have various causes, ranging in severity from ‘needs attention’ to ‘generally fatal’. By memorizing all the possibilities listed in this mnemonic, you can confirm or rule out the usual causes of RLQ pain to arrive at a correct diagnosis. The acronym A-P-P-E-N-D-I-C-I-T-I-S is easy to recall.
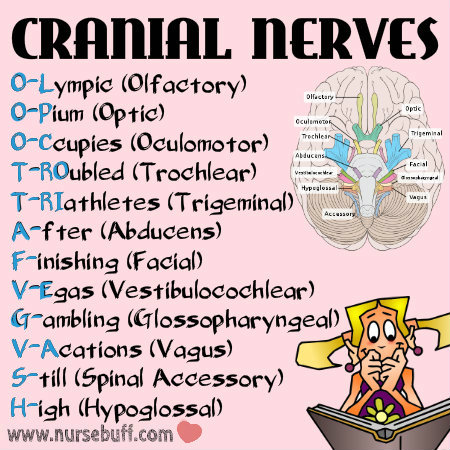
10. Cranial Nerves
It’s hard to remember the 12 cranial nerves without using an acronym. There are many mnemonics about this but the most effective one is Olympic Opium Occupies Troubled Triathletes After Finishing Vegas, Gambling Vacations Still High. The first two to three letter of this mnemonic will help you remember cranial nerves in order as showed in the medical mnemonic above.
11. Diabetic Ketoacidosis
The management and treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis is easy to remember with the mnemonic “KING UFC” as shown in the image above. Potassium is given to replace the serum potassium lost during osmotic diuresis. Insulin is given to stabilize blood sugar levels while glucose should also be on hand if ever blood sugar levels spike down.
For fluid replacement, crystalloids are best like 0.9% sodium chloride. In monitoring the patient’s condition during the treatment, urea and creatinine levels should be checked to determine impending renal failure.
 12. Diverticulitis
12. Diverticulitis
Diverticula are the little pouches that form in the inner lining of the intestine. The etiology behind the formation of these pouches is unknown but this condition is common among elderly.
Diverticulitis occurs once these pouches become inflamed. The pain during diverticulitis is concentrated in the left lower quadrant. To prevent this, the patient with diverticulosis should be in a low residue diet.
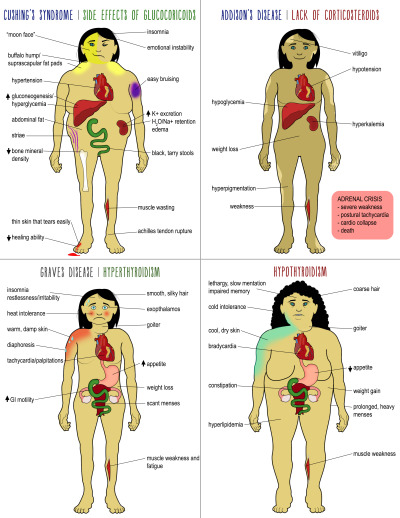
13. Endocrine Disorders
This is a quick overview of the four most common endocrine disorders. The upper part of the mnemonic details the two opposing adrenal disorders – Cushing’s syndrome and Addison’s disease. The bottom compares two opposing thyroid problems – hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism.
Cushing’s syndrome, also known as hypercortisolism, is a condition caused by prolonged exposure to cortisol. Those who are under glucocorticoid therapy are at risk for this syndrome. Addison’s disease, on the other hand, is a condition where the adrenal glands do not produce adequate glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids. If remained unresolved, the condition may lead to Addisonian crisis where hypotension and coma may occur.
Hyperthyroidism, also known as Grave’s disease, is an automimmune disease where there are high levels of circulating thyroid hormones in the body. Hypothyroidism, on the other hand, is a condition where the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones.
 14. 5 Areas for listening to the heart
14. 5 Areas for listening to the heart
There are five chest auscultation techniques – the aortic, pulmonic, Erb’s point, tricuspid and mitral points. These 5 areas for heart auscultation can be best remembered by the acronym All People Enjoy The Mall.
15. Head Injury
If a patient comes in reporting a head injury, you’ll have to closely observe the patient for signs and symptoms of worsening condition that may indicate severe brain injury. Here is a list of warning signs you should watch out for especially in the first 24 hours.
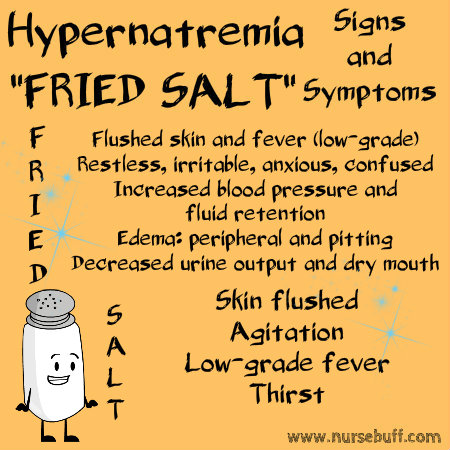
16. Hypernatremia – “You are FRIED”
Hypernatremia is an electrolyte imbalance in the body characterized by excessive levels of sodium in the blood. The signs and symptoms of this condition can be easily identified by the acronym “FRIED” – fever, restlessness, increased fluid retention and BP, edema and decreased urine output.
Usually, it is not caused by excess intake of sodium but rather by a decrease in total body water.
17. Drug Administration “DR. TIMED”
Remember the 6 rights of of drug administration using this colorful mnemonic. If you follow Dr. Timed to the letter, you should be able to avoid any problems or complications from administering medications.
18. Hypocalcemia signs and symptoms – CATS
Hypocalcemia is an electrolyte imbalance condition where the serum calcium level in the blood is low. This condition can be caused by hypothyroidism, chronic kidney disease and vitamin D deficiency. Signs and symptoms of this condition can be easily remembered with the mnemonic CATS – convulsions, arrhythmias, tetany, stridor and spasms.
19. Signs and Symptoms of Hypokalemia – “A SIC WALT”
Hypokalemia is a condition of abnormally low levels of potassium in the blood. The signs and symptoms of this condition is easy to remember with the mnemonic “ASICWALT” – alkalosis, shallow respirations, irritability, confusion and drowsiness, weakness and fatigue, arrhythmias, lethargy and thready pulse.
This electrolyte imbalance is usually caused by inadequate potassium intake, diarrhea and diuresis.
20. Level of Consciousness
The AVPU scale is a quick assessment tool for determining levels of consciousness. There are four ways on how you can assess patient’s responsiveness during emergency situations:
• Alert – the patient is fully awake and opens eyes spontaneously.
• Verbal stimuli – the patient responds to verbal stimuli and open eyes when you start talking.
• Painful stimuli – the patient only responds during the application of painful stimulus like sternal rub or squeezing of a finger.
• Unresponsive – the patient doesn’t show any kind of response to both verbal and painful stimuli.
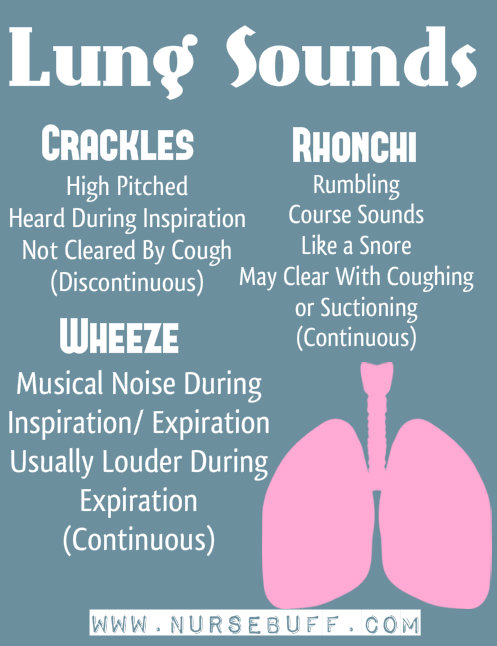
21. Lung Sounds
The three most common abnormal lung sounds are crackles, rhonchi and wheeze.
Crackles are similar to crackling or rattling sound. It is best heard during inhalation. The presence of crackles is usually suggestive of pneumonia and congestive heart failure.
Rhonchi resemble the sound of snoring. Its presence is suggestive of airway obstruction.
Wheezes resemble high pitch whistling sound. Its presence is suggestive of airway narrowing especially during asthma attacks.
22. Mixing Insulin
In mixing insulin, remember to draw up the clear first before the cloudy one. Fast-acting insulin is clear and should not be contaminated with long-acting insulin which is the cloudy one. Reminders in mixing insulin are detailed in this mnemonic.
23. Myocardial Infraction “BOOMAR” Nursing Management
The mnemonic “BOOMAR” is a great reminder in nursing management of myocardial infarction.
Complete bed rest is advised so there will be no additional workload for the heart. Oxygen therapy is essential to support adequate oxygen circulation in the blood. Opioids like morphine and anticoagulants are important in relieving chest pain and preventing further formation of blood clots. Close monitoring is a must through vital signs and other blood works so impending cardiac arrest can be anticipated and managed beforehand.
24. Neurovascular Assessment 5-Ps
In doing neurovascular assessment, remember the 5Ps – pain, pulse, pallor, paresthesia and paralysis. This assessment technique is useful in determining the presence of compartment syndrome among patients with casts or restrictive bandages.
25.Angina Precipitating Factors — 4 E’s
Angina is a symptom of an underlying heart condition. Patients who suffer from angina usually complain of tightness or discomfort in the chest area.
It is usually caused by unexpected or premature incidents you can recall as the 4E’s — sudden exertion, eating a huge meal, emotional distress, and extreme temperatures.
26. Nitroglycerin
Nitroglycerin is a potent vasodilator. It helps increase oxygen and blood flow to the heart by dilating the blood vessels. There are two types of nitroglycerin – quick-acting and slow-acting.
Quick-acting nitroglycerines are supplied in the form of sublingual tabs and translingual spray. On the other hand, slow-acting nitroglycerines are supplied in the form of patches, ointments and sustained-release tablets.
27. Phenylketonuria
Phenylketonuria is an inherited disorder where the body is unable to metabolize the enzyme phenylalanine causing buildup in the bloodstream. If left undetected, the buildup of phenylalanine in the blood may cause serious health problems like mental retardation and convulsions.
This condition can be easily detected at birth with routine newborn screening tests. Once confirmed, the child should have a diet free from meat, dairy products, eggs and other foods that contain protein.
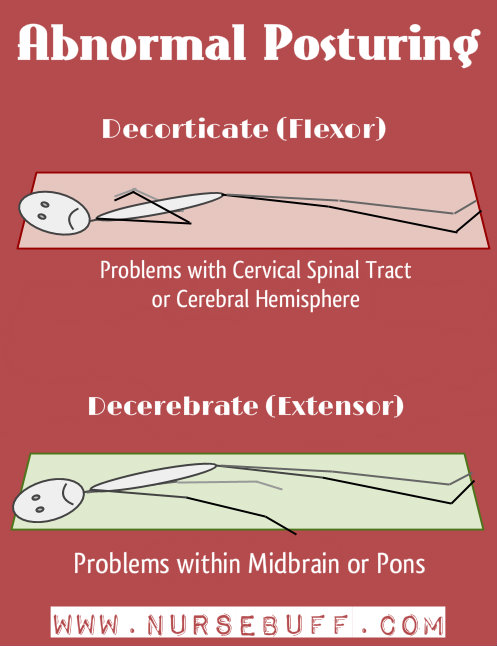
28. Posturing
Posturing is the abnormal flexion or extension of the arms and legs due to brain injury. There are two types of abnormal posturing – decorticate and decerebrate.
Decorticate posturing is characterized by flexed arms with inward bending in the chest area. The legs appear extended and both feet turn inward. Presence of decorticate posturing indicates damage to cervical spinal tract, thalamus and cerebral hemispheres.
Decerebrate posturing is characterized by extension of upper extremities particularly elbows and arching of the head backward. The legs are also extended and rotated internally. Presence of decerebrate posturing indicates damage in midbrain, brain stem and cerebellum.
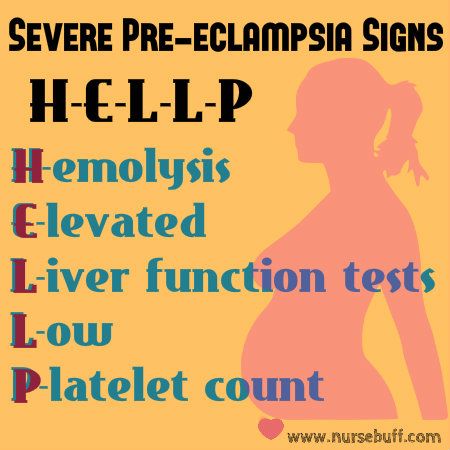
29. Severe Pre-eclampsia Signs – H-E-L-L-P
Pre-eclampsia is a pregnancy disorder characterized by high blood pressure, headache and proteinuria. If left untreated, severe signs and symptoms of pre-eclampsia are easy to remember with the acronym HELLP – hemolysis, elevated liver function tests and low platelet count.
Pre-eclampsia requires prompt medical attention as presence of HELLP symptoms indicate organ damage.
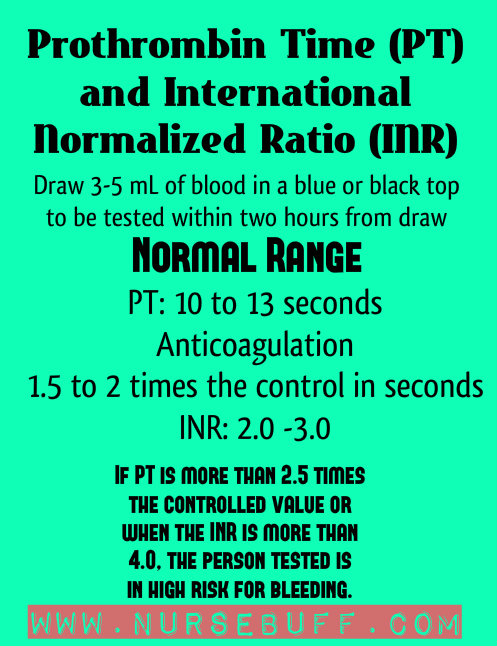
30. Prothrombin Time (PT) and INR
Prothrombin time (PT) assesses the extrinsic pathway of clotting. The measurement is expressed in seconds. Normal PT range is 10-13 seconds.
International Normalized Ration (INR) is calculated by dividing the patient’s PT values by a control. Normal INR range is 2.0 – 3.0.
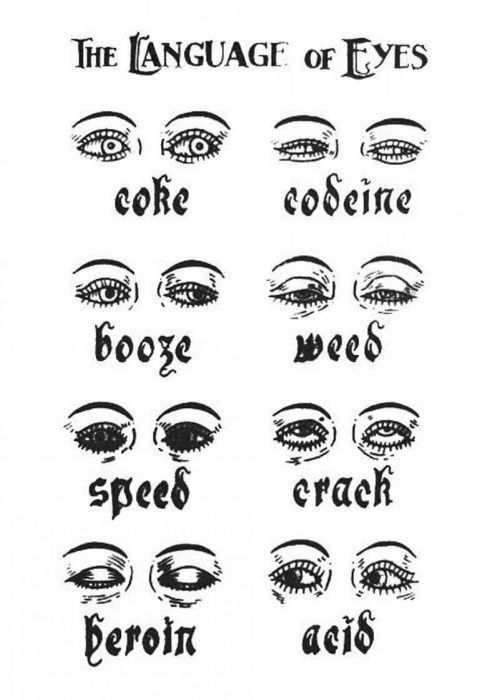
31. The Language of Eyes
This chart is useful in Emergency Nursing as different presentations of the eyes during substance abuse are specified. There are 6 addictive drugs in this chart – coke, codeine, booze, weed, speed, crack, heroin and acid.
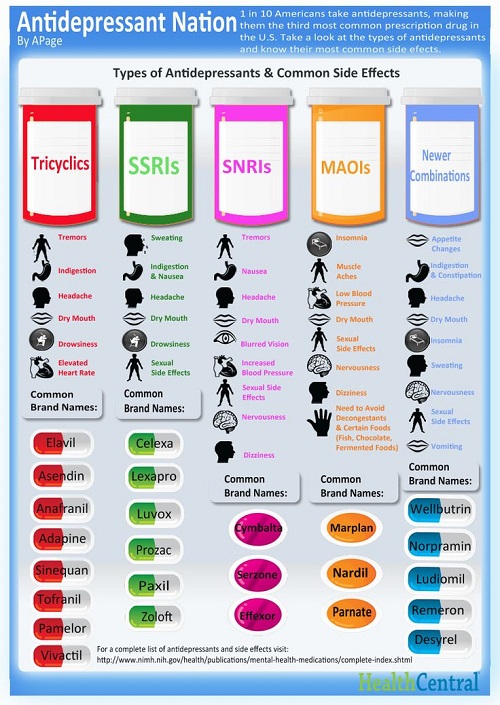
32. Types of Antidepressants and Common Side Effects
There are four types of anti-depressants – tricyclics, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) and monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). There are also new preparations being used as drug combinations like Wellbutrin and Norpramin.
Tricyclics block the reabsorption of serotonin and epinephrine in the nerve cells. Because of tricyclics’ effect in heart rate, patients with cardiac rhythm problems should not be given with these drugs.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) work by limiting the reabsorption of serotonin in the presynaptic cell thus increasing extracellular level of serotonin. SSRIs are mainly used to relieve major depression.
Serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) work by blocking the reuptake of both serotonin and norepinephrine. They also change the balance of other neurotransmitters in the brain.
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) inhibit monoamine oxidase, the enzyme that breaks down serotonin, dopamine and epinephrine. As a result, the levels of these neurotransmitters increase. However, when MAOIs are taken with other drugs, blood pressure levels may be adversely affected so it should be closely monitored.
 33. Congestive Heart Failure
33. Congestive Heart Failure
Congestive Heart Failure occurs when the heart cannot handle a high output of blood volume in the circulatory system. It is life-threatening so immediate treatment needs to applied. Remember the keys to initial management with the acronym UNLOAD FAST.
34. Calcium – Phosphorus Relationship
Calcium and phosphate in the body are like a seesaw. They react in opposite ways. When blood calcium levels rise, phosphate levels fall.
This relationship may be disrupted by an infection or a disease so it is important to measure calcium and phosphorus at the same time.
With these medical mnemonics for NCLEX and other nursing examinations, you can now prepare for your test or your nursing classes. There are lots of mnemonics available online that can be helpful in remembering difficult nursing concepts. Whenever you are tired of reading your textbooks and notes, take a break and have fun learning with medical mnemonics.
Don’t forget to drop by our FB page or Instagram anytime!
(Editor’s Note: Hello dear readers! We’re missing a handful of mnemonics from our original 50. We’re revamping this list and we’ll be adding in brand new mnemonics very soon!)