Auscultation of Heart Sounds
There are two important reminders in auscultating heart sounds – the S1 or the first heart sound is loudest at the apex of the heart while S2 sounds or the second heart sounds are loudest at the base of the heart.
The S1 results from the closing of AV valves and this is the reason why it can be heard loudest at the base of the heart. The S2 sounds result from the closure of semilunar valves and these sounds can be heard prominently at the apex of the heart.
Study Guide:
Heart Auscultation – Patient.co.uk
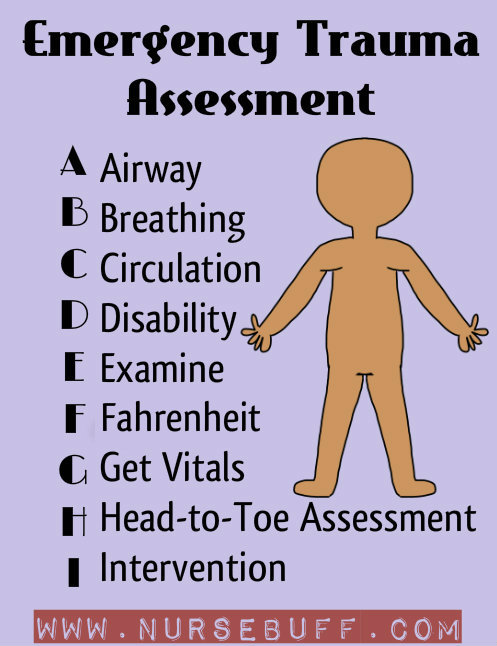
Emergency Trauma Assessment
During emergency trauma accidents, proper assessment can be easily remembered with the alphabetical letters A-I.
- Airway – check for patency of airway. Make sure that there is no obstruction along the airway passages.
- Breathing – is the patient still breathing? Check for the quality of breathing pattern if it’s too fast or to shallow.
- Circulation – checking for the pulse, heart rate and blood pressure will ensure if the blood circulation within the body is not compromised.
- Disability – check if the patient can fully move his limbs. Check the five senses – vision, hearing, smell, taste, and touch. Assess the level of consciousness of the patient if he is fully awake and oriented.
- Examine – visually examine the patient for problems. Look for wounds, fracture and other physical problems.
- Fahrenheit – check the patient’s temperature if there is hyperthermia or hypothermia.
- Get Vitals – obtain patient’s vital signs like temperature, heart rate, respiratory rate and blood pressure.
- Head-to-toe assessment – conduct physical assessment from head-to-toe. Determine body symmetry.
- Intervention – for the problems detected after completing your assessment, prioritize planned interventions. Conducting first-aid interventions is beneficial before transferring the patient into proper medical facilities.
Study Guides:
Trauma Assessment – Patient.co.uk
Trauma Assessment for the EMT – EMSWorld.com
The 60 Second Patient Assessment in Trauma – EMRA
Hyperkalemia
Hyperkalemia is a condition where there is an abnormally high level of potassium in the blood.
Signs and symptoms that should be observed when assessing a patient for hyperkalemia include muscle cramps, muscle twitches, paresthesias, irritability, decreased blood pressure, ECG changes, dysrhythmias, abdominal cramps and diarrhea.
ECG readings of patients with hyperkalemia will reveal prolonged PR segment, flat P, widened QRS segment, peaked T and depressed ST segment.
Study Guides:
Hyperkalemia Definition and Symptoms – Mayo Clinic
High Potassium Level – MedlinePlus
Hypokalemia
Hypokalemia is a condition where there is an abnormally low level of potassium in the blood.
Symptoms include alkalosis, shallow respirations, irritability, confusion, drowsiness, weakness, fatigue arrhythmias, lethargy, thread pulse and decreased intestinal motility.
Changes in ECG may also be observed where there will be abnormality in QRS segment.
Study Guides:
Hypokalemia Definition and Symptoms – Mayo Clinic
Hypokalemia Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatments – Clinical Key
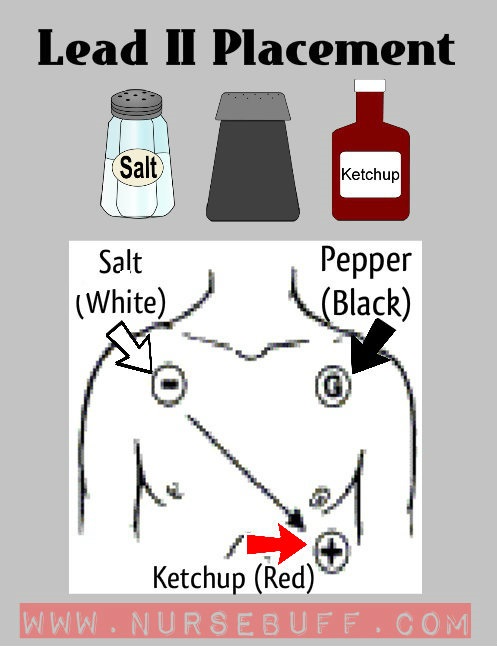
Lead II Placement
Lead II placement can be easily remembered with the mnemonic salt, pepper and ketchup.
The white lead should be placed in the right part of the chest while the black lead is in the left part of the chest. The red lead should be placed below the black lead as pictured below.
Study Guides:
ECG Learning Center – An introduction to clinical electrocardiography
Electrode Placement and Lead Selection
Levels of Consciousness
The AVPU mnemonic is a mnemonic used by first aiders in quickly assessing the level of consciousness of the patient.
- Alert – the patient is fully awake and opens the eyes spontaneously.
- Voice – the patients responds to verbal stimuli or only when you talk.
- Pain – the patient only responds when a painful stimulus is elicited. The sternal rub and squeezing of the fingers are the two most commonly used painful stimuli in assessing the level of consciousness.
- Unresponsive – also known as unconscious, the patient is considered unresponsive when there is no response obtained after eliciting verbal and painful stimuli.
Study Guides:
AVPU – Emergency Medical Paramedic
AVPU Scale – Family Practice Notebook
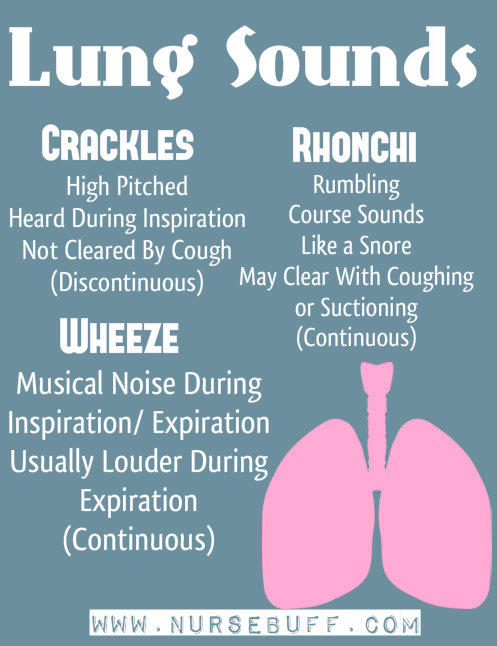
Lung Sounds
There are three abnormal lung sounds that can be heard during respiratory problems – crackles, rhonchi and wheezes.
Crackles are high-pitched sounds heard during inspiration. It resembles the cracking or rattling sounds.
Rhonchi, on the other hand, are rumbling course sounds heard during inspiration or expiration. It can be cleared when coughed out or when phlegm is suctioned out.
Wheezes are musical-like sounds heard during inspiration or expiration. It resembles whistling sounds and it can be heard louder during expiration.
Study Guide:
Breath Sounds – Colorado State University
Neurovascular Assessment
There are five Ps essential in conducting neurovascular assessment – pain, pulse, pallor, paresthesia and paralysis.
Start by assessing if there is pain felt within the affected area. Then check for symmetry of pulses especially if it’s weak or thready. Visually inspect for pallor. Determine if there is paresthesia by eliciting stimuli along the affected area. Lastly, check for paralysis by asking the patient to move the affected part.
Study Guide:
Neurovascular assessment – SNJourney.com