1. Cane Walking.

When assisting a patient who is using a cane, make sure that the cane has been adjusted to the patient’s height. Also, the handle should be at the level of the wrist, and the elbow should be slightly bent when holding the handle.
When walking with a cane, the patient must stand with a firm grip on the cane. Upon stepping forward with the weaker leg, the cane must be swung at the same distance in front. The tip of the cane and the forward foot must be even.
2. Chest Tube.

If a chest tube is pulled out of the patient accidentally, an occlusive dressing is used over the wound to avoid re-entry of air. The occlusive dressing should be taped on only three sides and should immediately be placed over the insertion site. This allows air to escape and reduce the risk for development of a tension pneumothorax.
3. Delegation to Unlicensed Assistive Personnel (UAP).

Nurses usually delegate to unlicensed assistive personnel (UAPs), but they must remember to delegate legally, safely and effectively.
To do this, certain rules must be kept in mind. Nurses should know the scope of their practice, the policies and procedures regarding delegation, the UAP’s abilities, and the type of patients they’re handling. You should not delegate unstable patients and basic Nursing activities such as assessment, teaching, medication administration, and evaluation.
4. Basics of Delegation.

Delegation of certain tasks must always be based on principles of public protection. There are five rights of delegation: right task, right circumstances, right person, right direction/ communication, and right supervision/ evaluation.
Licensed nurses should remember that they have the ultimate accountability for the management and provision of nursing care, including all delegation decisions.
5. Drawing Insulin.

When mixing and drawing two types of insulin, there are few basic steps you need to remember.
First, make sure to draw air into the syringe equal to the amount of NPH insulin (cloudy) that you need, then pushing all of the air into the NPH insulin bottle. Next, you have to draw air into the syringe again, this time, equal to the amount of Novolog/Humanog (clear) insulin that you need, then pushing all the air into the regular insulin bottle.
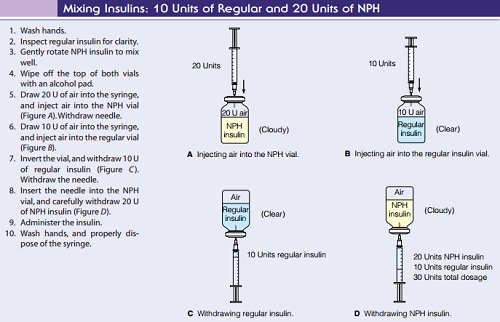
Draw up the number of units of insulin that you need for the Novolog/Humalog dose, before going to the NPH bottle and drawing up the amount of NPH (cloudy) insulin necessary.
6. Eyes.

Visual acuity is the clearness of vision or the quantitative measure of the ability to identify black symbols on a white background. In optometry and nursing, the most commonly used abbreviations are OU (both eyes), OS (left eye), and OD (right eye).
7. Hypernatremia.

Hypernatremia is a condition characterized by high levels of sodium (greater than 145) and too little water in the body. Risk factors include not getting enough fluids, fever, vomiting, diarrhea, diuretics, severe burns, losing too much fluid, aging, and certain medical condition such as diabetes or kidney disorder.
Also Read: 5 Nursing Mnemonics & Acronyms (Acid-Base, Fluids, & Electrolytes)
Signs and symptoms of hypernatremia include thirst, dry mouth, muscle weakness or cramps, decreased urination, weight loss, lightheadedness, irritability, confusion, and muscle twitching.
8. IM Injection in Neonate.

The preferred site for IM injection in infants under 12 months old is the anterolateral thigh. Medications must be injected into the bulkiest part of the vastus lateralis or thigh muscle. Using the vastus lateralis muscle avoids the risk of sciatic nerve damage from gluteal injection.
Also Read: How To Perform IV Insertion On Pediatric Patients
9. Intake and Output.
Intake is anything that goes into the patient’s body that is measurable, while output is any fluid that comes from the patient’s body that can be measured. Both are measured in Milliliters (mL) or cubic centimeters (cc).
10. Positive PPD (Mantoux) Test.

A positive Tuberculin skin test (Mantoux) does not mean that a contagious or active infection is present. The test will not be able to tell precisely whether an infection is active or inactive. Additional tests such as chest X-ray, sputum culture, or both, may be required to confirm an active Tuberculosis infection.
11. Postural Drainage.

Postural drainage is often used together with chest physiotherapy in conditions such as cystic fibrosis or spinal cord injury to help loosen and remove mucus from the lungs, lowering the risk of getting lung infections.
12. Potassium Imbalances.

Alkalosis is a condition in which the body fluids have excess base. Hypokalemic alkalosis refers to the loss of too much potassium, which is usually caused by severe vomiting.
Acidosis, on the other hand, is a condition in which there is an overabundance of acids in the blood. In acidosis, hydrogen ions move from the circulation into the cells in exchange for potassium to reduce the acidity of the blood. This exchange may relieve the severity of acidosis, but it may cause an abnormally high level of blood potassium.]
13. Signs of Hypocalcemia.

Hypocalcemia occurs when the total serum Ca concentration is less than 8.8 mg/dL in the presence of normal plasma protein concentrations. It is usually caused by excessive calcium loss in the urine or a failure to move calcium out of the bones into the bloodstream.
Chvostek sign is the twitching and/or contracture of the facial muscles when a specific point on the face is tapped. Trousseau’s sign, on the other hand, is the carpopedal spasm occurring a few minutes after inflation of a sphygmomanometer cuff above systolic blood pressure.
14. Russell’s Traction.

Russell’s Traction is a form of skin traction involving a system of suspension and traction. Like in Buck’s extension, adhesive strips are applied and the knee is suspended in a sling. The advantage of Russell’s traction is that some movement in bed is permissible.
15. Sprain and Strain.
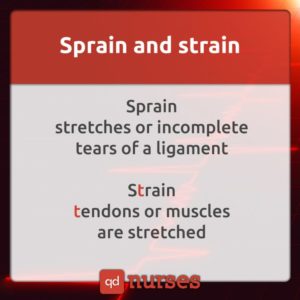
A sprain is a stretched or torn ligament. Common causes of sprains are falling, twisting, or getting hit. Symptoms include pain, swelling, bruising, and inability to move joint.
A strain, on the other hand, is an injury of a muscle or tendon. Strains can happen suddenly or develop over time. Symptoms include pain, muscle spasms, swelling, and difficulty in moving the muscle. The most common strains are back and hamstring muscle strains.
16. Stridor.

Stridor is an abnormal, high-pitched, musical breathing sound usually caused by a blockage in the throat or larynx.
Other common causes include abscess on the tonsils, airway injury, allergic reaction, croup, foreign body aspiration, laryngitis, neck injury, use of a breathing tube for a long period of time, secretions, smoke inhalation, swelling of the neck or face, swollen tonsils or adenoids, and vocal cord cancer.
17. Tracheostomy Tube Cuff.

A tracheostomy cuff is a balloon around the outside of the tracheostomy tube which is filled with air so that it fits the shape of your trachea.
Also Read: 35+ Tracheostomy Care Techniques for Nurses
The balloon seals off the space between the wall of the trachea and the tracheostomy tube, which is needed when the patient is on a breathing machine (ventilator) or is having problems with choking. If the cuff is not inflated, air can pass around the tracheostomy tube.
18. Diarrhea and Vomiting.

Metabolic acidosis refers to a condition where there is too much acid in the body fluids. It occurs when the body produces too much acid, or when the kidneys are not removing enough acid from the body.
Metabolic alkalosis, on the other hand, is when there is too much bicarbonate in the blood and usually occurs due to kidney diseases. It can also occur due to prolonged vomiting, sweating as well as ingestion of too much bicarbonate.
See More:
1. Nursing Flashcards (Communicable Diseases)
2. Nursing Flashcards (Diagnostics and Lab Procedures)
3. Nursing Flashcards (NCLEX Tips/ Psychiatric Nursing)
4. Nursing Flashcards (Medical-Surgical Nursing)
5. Nursing Flashcards (Nutrition)
6. Nursing Flashcards (Obstetrics and Newborn Care)
7. Nursing Flashcards (Pediatric Nursing)
8. Nursing Flashcards (Pharmacology)